Fig. 2.
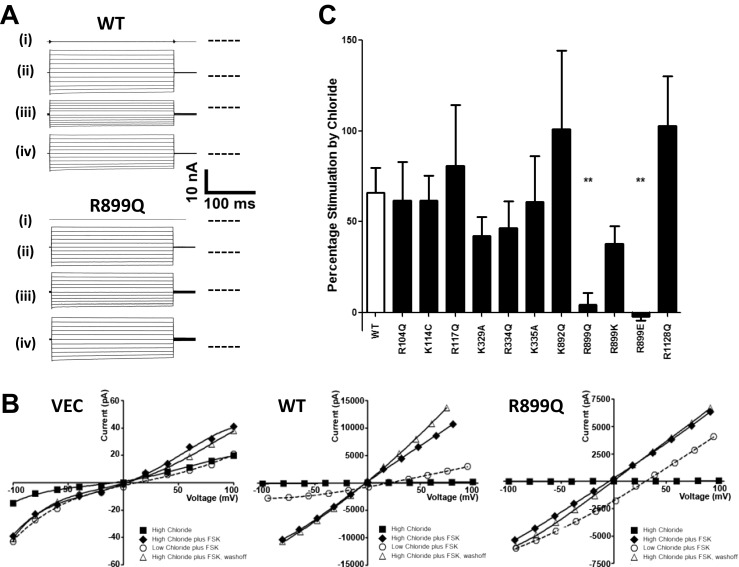
Arginine residue 889 in extracellular loop 4 of CFTR is essential for [Cl−]o sensing. a Representative fWCR current recordings measured between ±100 mV in 20 mV steps from HEK cells transfected with wild type (WT) CFTR and R899Q CFTR, as indicated. The current traces are from the top down: (i) unstimulated in 155.5 mM [Cl−]o, (ii) forskolin (FSK)-stimulated in 155.5 mM [Cl−]o, (iii) FSK-stimulated in 35.5 mM [Cl−]o and (iv) FSK-stimulated in 155.5 mM [Cl−]o. Dotted line to the right of the current traces indicates zero current level. b Representative I-V plots for the Vector Control (VEC), WT and R899Q CFTR, for unstimulated in 155.5 mM [Cl−]o (black squares); FSK-stimulated in 155.5 mM [Cl−]o (black rhombus); FSK-stimulated in 35.5 mM [Cl−]o (white circles) and FSK-stimulated in 155.5 mM [Cl−]o washoff (white triangles). I-V plots were obtained from whole cell currents in a. All constructs, except the vector control, showed positive E rev shifts (see Table 1) on switching to low [Cl−]o consistent with the expression of a Cl−-selective conductance. Note the different y-axis scales for the respective I-Vs. c Percentage stimulation of FSK-activated currents by [Cl−]o for WT CFTR (n = 24) and for different extracellular loop mutants (see Fig. 1a) (n = 4–9). Percent stimulation was calculated from I-V data at −60 mV from the reversal potential, as described in “Materials and methods.” Data are means ± SEM. **p < 0.01 compared to WT CFTR
