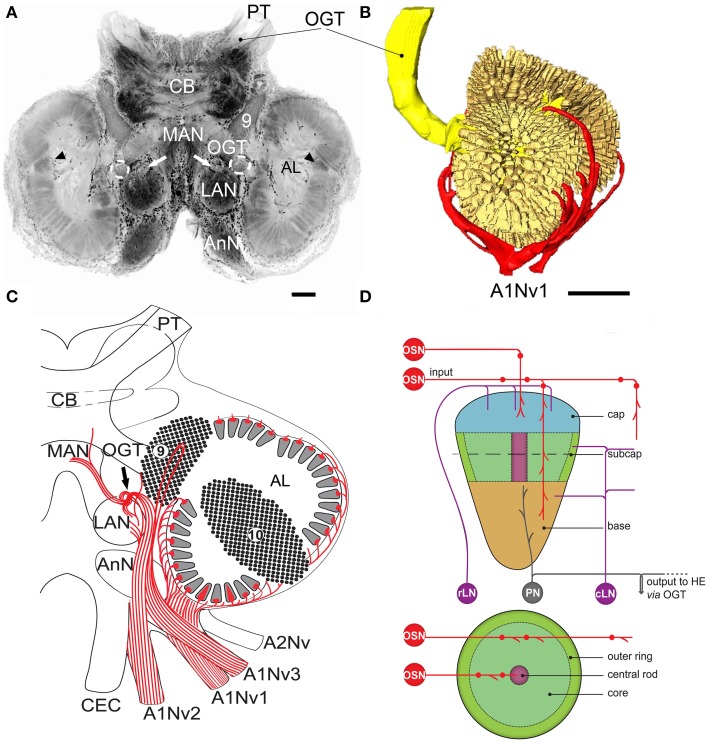
Figure 1.
Overview of C. clypeatus median brain as seen in confocal laser scanning microscopy, cLSM (anti-synapsin immunohistochemistry), arrowheads mark non-columnar olfactory neuropils and arrows on (A,C) mark a sorting zone for A1Nv2 fibers (see text). (A) 3D-reconstraction of the antennular lobe, showing olfactory afferents (in red) invading numerous subunits (pale yellow), and axons of the projection neurons (bright yellow) leaving the antennular lobe via olfactory-globular tract and reaching for the higher brain centers; (B) Overview of the central projections of antennular nerve (red). (C) Schematic representation of the subunits regionalization into cap, subcap, and base in longitudinal section and outer ring, core, and central rod in transverse section. The projection patterns of the olfactory afferents are shown in red; local interneurons in magenta and projection neurons in gray (D). PT, protocerebral tract; OGT, olfactory-globular tract; CB, central body; MAN, LAN, median and lateral antennular neuropil correspondingly; AnN, antenna 2 neuropil; CEC, circumesophageal connectives; A1Nv1, A1Nv2, A1Nv3, branches of the antennular nerve; A2Nv, antenna 2 nerve; AL, antennular lobe; OSN, olfactory sensory neurons; rLN, rim local interneurons; cLN, core local interneurons; PN, projection neurons; HE, hemielipsoid body; 9, cell cluster 9, local interneurons; 10, cell cluster 10, projection neurons. Scale bars: 100 μm on A, 250 μm on B.