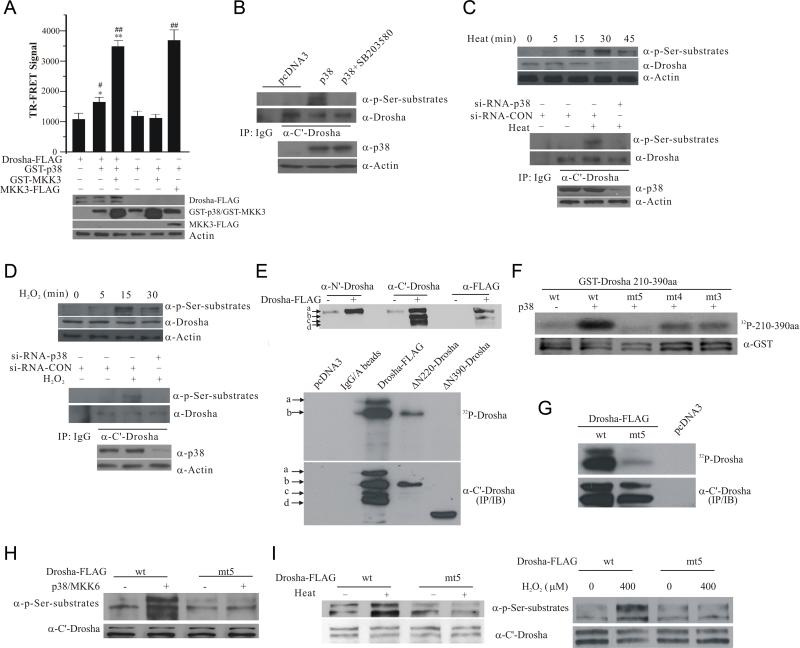
Figure 1.
Phosphorylation of Drosha RS-rich domain by p38 MAPK. (A) Interaction between Drosha and p38 by TR-FRET. HEK293 cells were transfected with various plasmids carrying Drosha-FLAG, FLAG-MKK3, GST-p38 and GST-MKK3. Over-expressed proteins immunoprecipitated from lysates were tested for TR-FRET signal. The top panel shows TR-FRET signal expressed as ratio (A665/A615 × 104). The data were expressed as mean ± SD from triplicate samples (*p <0.05 or **p < 0.01 vs Drosha-FLAG alone group and #p < 0.05 or ##p < 0.01 vs GST-p38 alone group; ANONA with Dunnett's Test). The bottom panel shows the expression of Drosha-FLAG, GST-p38, GST-MKK3, and FLAG-MKK3. (B) p38 MAPK-induced phosphorylation of endogenous Drosha. Endogenous Drosha immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells transfected as indicated was blotted with an anti-phospho Ser followed by a proline (top panel). The bottom panel shows the levels of p38. (C) Heat-induced phosphorylation of endogenous Drosha in HEK293 cells. Levels of phosphorylated Drosha in cellular lysates were measured by anti-phospho Ser blotting after heat (45°C) treatment (top panel). Drosha immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells transfected and treated with heat for 15 min was blotted with anti-phospho Ser antibody (middle and bottom panels). (D) H2O2-induced phosphorylation of endogenous Drosha in HEK293 cells. The experiments were carried out as described in (C) with H2O2 (400 μM) treatment of various time (top panel) or 15 min. (E) Mapping the phosphorylation domain of Drosha by direct p38 kinase assay. Top panel shows multiple species of Drosha-FLAG marked as a-d recognized by the indicated antibodies in HEK293 lysates over-expressing Drosha-FLAG. Middle panel shows the autoradiograph of in vitro p38 MAPK kinase reaction with Drosha-FLAG, ΔN220-Drosha-FLAG and ΔN390-Drosha-FLAG immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells with the anti-C’ Drosha antibody. The same membrane was probed by anti-C’ terminal Drosha antibody (bottom panel). (F) Identification of p38 phosphorylation sites in Drosha RS-rich domain. Purified GST-Drosha 210-390aa was incubated with purified p38 MAPK in kinase assay (top panel, autoradiograph). The same membrane was blotted with an anti-GST antibody (bottom panel) (wild type: wt; mutants: mt3, S220A, S255A, and T274A; mt4, S220A, S255A, T274A, and S300A; and mt5, S220A, S255A, T274A, S300A, and S355A). (G) Phosphorylation of Drosha by p38 MAPK. Drosha-FLAG (wt and mt5) was immunoprecipitated from cells with anti-C’ terminal Drosha antibody and phosphorylated by p38 MAPK in vitro. (H) Phosphorylation of Drosha by p38 MAPK in cells. Cell lysates from HEK293T cells transfected as indicated were blotted with the phospho Ser antibody. The same membrane was re-probed with anti-C’ Drosha antibody. (I) Heat- or H2O2-induced phosphorylation of Drosha. HEK293T cells after transfection were treated with heat (45°C) or H2O2 (400 μM) for 15 min. Lysates were blotted as described in (H). See also Figure S1.