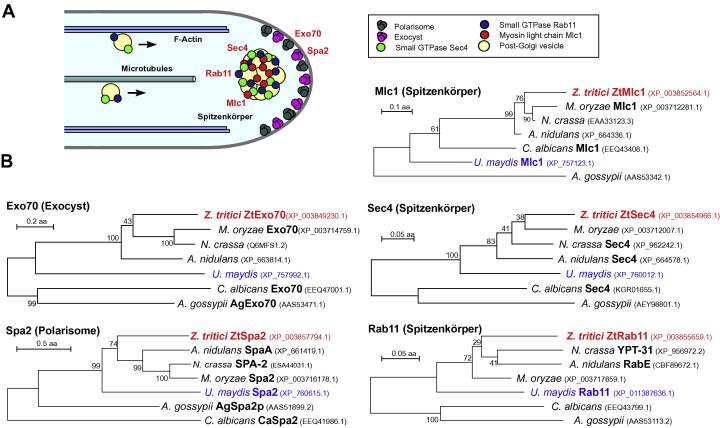
Fig. 1.
Cell polarity markers in Z. tritici. (A) Schematic drawing of a growing hyphal tip of a filamentous fungus. Post-Golgi vesicles are delivered by the cytoskeleton to the hyphal tip. In many fungi, they accumulate in the apical Spitzenkörper. The myosin light chain Mlc1 and the small GTPases Sec4 and Rab11/Ypt-31 concentrate in the Spitzenkörper. The exocyst complex is thought to support tethering of secretory vesicles at the plasma membrane and localizes in an apical cap in most fungi. A similar localization is described for the polarisome protein Spa2. The diagram is based on published data in several fungi, including N. crassa (Sanchez-Leon et al., 2015; Araujo-Palomares et al., 2009), A. nidulans (Virag and Harris, 2006b; Pantazopoulou et al., 2014), M. oryzae (Giraldo et al., 2013), C. albicans (Jones and Sudbery, 2010), A. gossypii (Köhli et al., 2008), U. maydis (Carbo and Perez-Martin, 2008), A. niger (Meyer et al., 2008). Note that Exo70 in N. crassa does not form an apical cap, but localizes to the Spitzenkörper (Sanchez-Leon et al., 2015). The same localization was found in A. gossypii fast-growing hyphae (Köhli et al., 2008). In these cells, Spa2 is also concentrated in the Spitzenkörper (Köhli et al., 2008). This corresponds with a partial co-localization of Spa2 and the Spitzenkörper in N. crassa and A. nidulans was reported (Lichius et al., 2012; Virag and Harris, 2006a,b). (B) Phylogenetic trees comparing the predicted full-length amino acid sequence of fungal homologues of the exocyst protein Exo70, the polarisome protein Spa2, the vesicle associated GTPase Sec4, the myosin-light chain Mlc1 and the GTPase Rab11/Ypt31. The Z. tritici orthologues, used in this study, are indicated in bold and red. The basidiomycete U. maydis is indicated in blue. Where available, published protein names are provided in bold. NCBI accession numbers are given behind species names (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed). Maximum likelihood trees were generated using MEGA5.2 (Tamura et al., 2011). Bootstrap values are indicated at branching points.