Fig. 2.
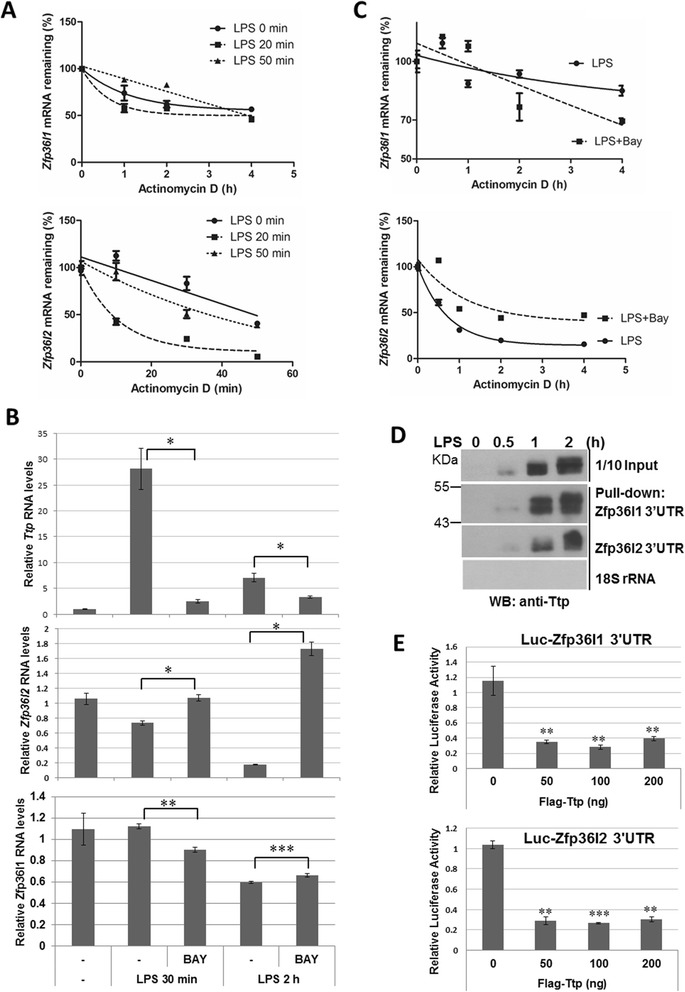
mRNA stability regulation of Zfp36l2 by Ttp during LPS-stimulation. a mRNA half-life determination. RAW264.7 cells stimulated with LPS for 0, 20 and 50 min, and actinomycin D (10 μg · mL-1) was added for 0, 10, 30, and 50 min to stop transcription for Zfp36l2 mRNA detection, and added for 0, 1, 2 and 4 h for Zfp36l1 mRNA detection. RNAs was isolated for quantitative PCR by using primers of β-actin, Zfp36l1 and Zfp36l2. The remaining Zfp36l1 and Zfp36l2 mRNA levels were shown after normalized with the level of β-actin. The mRNA half-lives were calculated by exponential regression: 5.2 h, 4.2 h, and 3.5 h for Zfp36l1 at 0, 20 min, and 50 min of LPS treatment, respectively; 39 min, 13 min and 33 min for Zfp36l2 at 0, 20 min, and 50 min of LPS treatment, respectively. b TTP family mRNA analysis under BAY treatment. RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with or without 20 μM of BAY for 0.5 h followed by adding 100 ng · mL-1 LPS for 0.5 and 2 h. Total RNAs were isolated for quantitative PCR. c BAY treatment stabilizes Zfp36l2 mRNA. RAW264.7 cells pretreated with or without 20 μM of BAY for 0.5 h followed by adding 100 ng · mL-1 LPS for 20 min, and actinomycin D was added for 0, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 h to stop transcription. RNAs was isolated for quantitative PCR and Zfp36l1 and Zfp36l2 mRNA half-lives were determined. d RNA pull-down analysis. Biotin labeled Zfp36l1 3’UTR, Zfp36l2 3’UTR and control 18S RNA were incubated with cytosolic extracts from RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS for 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 h, respectively. After extensive washes, the RNA-protein complexes were analyzed by western blotting with anti-Ttp. e Luciferase reporter analysis. 293 T cells were cotransfected with of 0.25 μg Zfp36l1 3’UTR- or Zfp36l2 3’UTR-containing luciferase reporter and different amounts of Flag-tagged Ttp expression plasmid. After normalized with internal control of Renilla luciferase activity, the relative firefly luciferase activity was shown. All experiments were independently repeated at least two times
