Abstract
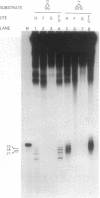
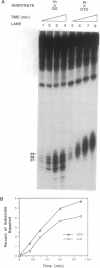
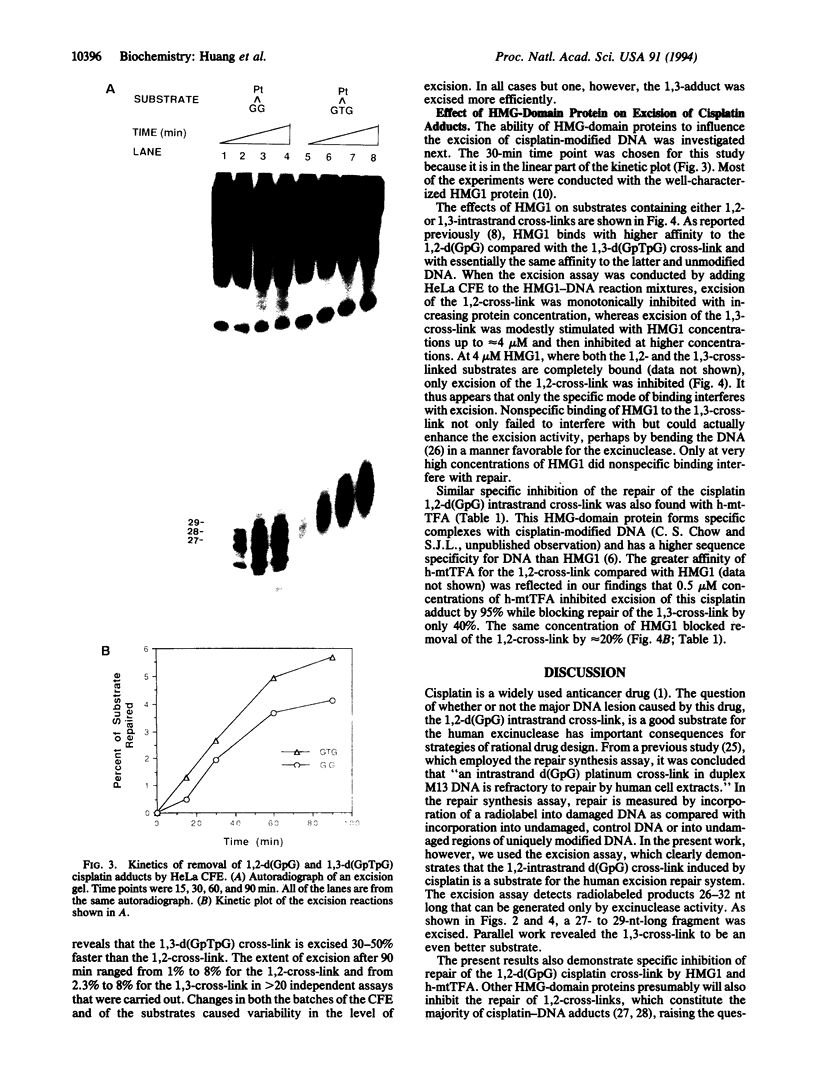
The most frequent DNA adduct made by the anticancer drug cisplatin, the 1,2-intrastrand d(GpG) cross-link, as well as the minor 1,3-intrastrand d(GpTpG) adduct, were both repaired by an in vitro human excision repair system. Fragments of 27-29 nt containing the platinum damage were excised. The high mobility group (HMG)-domain proteins HMG1 and human mitochondrial transcription factor specifically inhibited repair of the 1,2-intrastrand cross-link by the human excision nuclease. These results suggest that the types and levels of HMG-domain proteins in a given tumor may influence the responsiveness of that cancer to cisplatin chemotherapy and they provide a rational basis for the synthesis of new platinum anticancer drug candidates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck D. J., Brubaker R. R. Effect of cis-platinum(II)diamminodichloride on wild type and deoxyribonucleic acid repair deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1247–1252. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1247-1252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E. Production of functional rat HMG1 protein in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. J., Kellett P. J., Lippard S. J. Ixr1, a yeast protein that binds to platinated DNA and confers sensitivity to cisplatin. Science. 1993 Jul 30;261(5121):603–605. doi: 10.1126/science.8342024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn S. L., Pil P. M., Essigmann J. M., Housman D. E., Lippard S. J. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding a high mobility group box protein that recognizes structural distortions to DNA caused by binding of the anticancer agent cisplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Lehn D. A., Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90092-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. The formation, isolation and characterization of DNA adducts produced by anticancer platinum complexes. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;34(2):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtinger-Schepman A. M., van Oosterom A. T., Lohman P. H., Berends F. cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-induced DNA adducts in peripheral leukocytes from seven cancer patients: quantitative immunochemical detection of the adduct induction and removal after a single dose of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):3000–3004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraval H. N., Rawlings C. J., Roberts J. J. Increased sensitivity of UV-repair-deficient human cells to DNA bound platinum products which unlike thymine dimers are not recognized by an endonuclease extracted from Micrococcus luteus. Mutat Res. 1978 Jul;51(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Giese K., Pagel J. HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Sancar A. Determination of minimum substrate size for human excinuclease. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19034–19040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehrer P. J., Einhorn L. H. Drugs five years later. Cisplatin. Ann Intern Med. 1984 May;100(5):704–713. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-5-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraw T. L., Chae C. B. Functional complementarity between the HMG1-like yeast mitochondrial histone HM and the bacterial histone-like protein HU. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12758–12763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):965–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2035027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Xu B., Clayton D. A. A human mitochondrial transcriptional activator can functionally replace a yeast mitochondrial HMG-box protein both in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1951–1961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Thompson L. H., Sancar A. Excision repair in man and the molecular basis of xeroderma pigmentosum syndrome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:605–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Tang M. S. Nucleotide excision repair. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 May;57(5):905–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb09233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. The effects of covalent additions of a psoralen on transcription by E. coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6843–6854. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda D. L., Taylor J. S., Hearst J. E., Sancar A. DNA repair by eukaryotic nucleotide excision nuclease. Removal of thymine dimer and psoralen monoadduct by HeLa cell-free extract and of thymine dimer by Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1931–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymkowski D. E., Yarema K., Essigmann J. M., Lippard S. J., Wood R. D. An intrastrand d(GpG) platinum crosslink in duplex M13 DNA is refractory to repair by human cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10772–10776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Wood R. D. Xeroderma pigmentosum and nucleotide excision repair of DNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90040-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Busch D. B., Brookman K., Mooney C. L., Glaser D. A. Genetic diversity of UV-sensitive DNA repair mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]