Fig. 1.
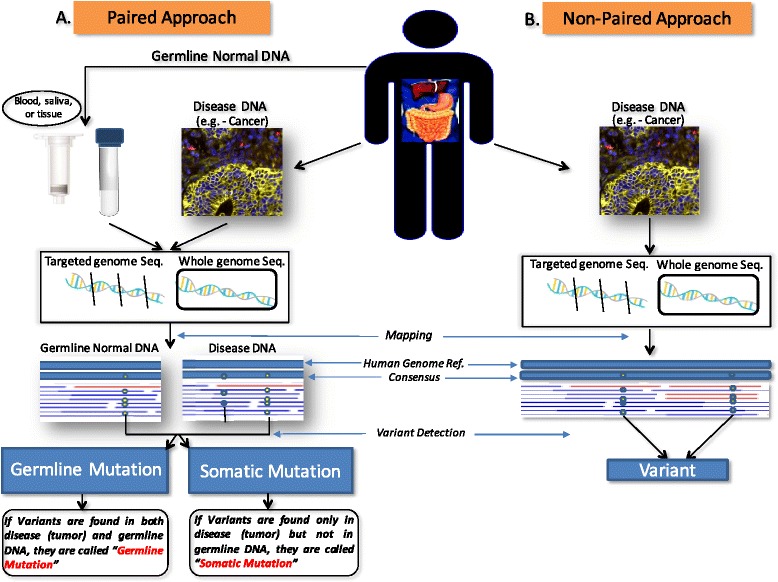
Nomenclature of variants according to sequencing design. In a paired approach (a), diseased (tumor) DNA and DNA from the germline (blood, saliva, or other non-diseased tissue) have been extracted and individually sequenced and mapped against a human genome reference assembly. If there are common variants found in both the tumor and germline DNA, they should be called germline mutations. If there are variants found only in tumor DNA, they should be called somatic mutations. In a non-paired approach of variant detection (b), only diseased DNA is extracted from the tissue of interest. The extracted DNA has been sequenced and mapped against a human genome reference assembly and differences as compared with the reference will be labeled as variants
