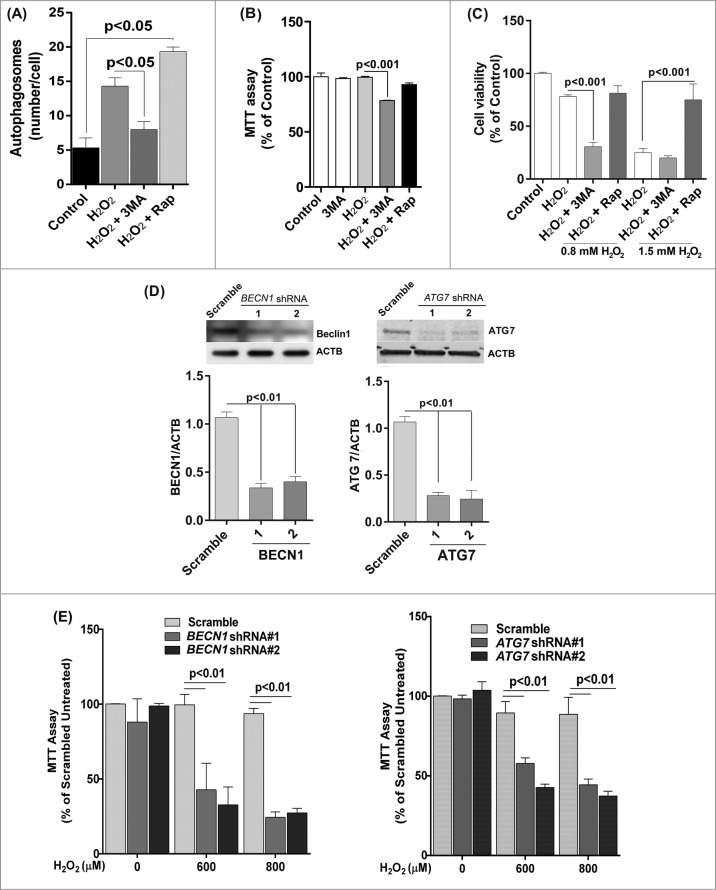
Figure 5.
Reduced autophagy renders ARPE-19 cells more susceptible to oxidative stress while increased autophagy protects cells against oxidative stress. (A) Autophagosome counts in ARPE-19 cells treated for 12 h with 3-MA (10 mM) or rapamycin (100 nM) and treated with H2O2 (400 μM) for 3 h were obtained following immunostaining with LC3 antibody to identify autophagic puncta. (B) ARPE-19 cells were pretreated for 12 h with 3-MA (10 mM) or rapamycin (100 nM) and treated with H2O2 (400 μM) for 3 h after which mitochondrial respiratory activity was determined using the MTT assay. Differences between means were considered statistically significant from 4 independent experiments when P < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA. (C) The crystal violet assay was performed on 3-MA and rapamycin pretreated RPE cells and subsequently exposed to 0.8 and 1.5 mM H2O2. Differences between means were considered statistically significant from 4 independent experiments when P < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA. (D) BECN1 and ATG7 knockdown by lentiviral shRNAs in RPE was confirmed by protein gel blot. Knockdown was considered statistically significant when P < 0.01 from at least 3 independent experiments (E) The MTT assay was performed on ARPE-19 cells with BECN1 or ATG7 knockdown to assess the cell viability in response to increasing concentrations of H2O2. Differences between means were considered statistically significant from 4 independent experiments when P < 0.05 or 0.01 using one-way ANOVA.