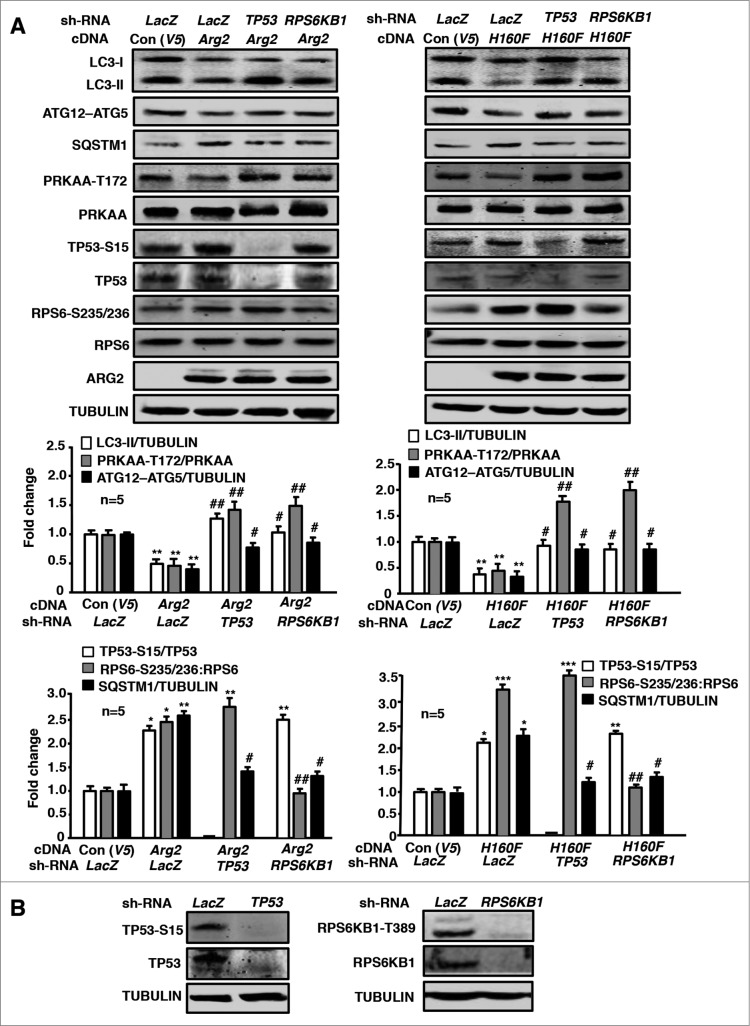
Figure 3.
Silencing RPS6KB1 or TP53 in young HUVECs attenuates ARG2-induced inhibition of PRKAA signaling and autophagy suppression. Young HUVECs were first transduced either with rAd/U6-LacZshRNA as control, rAd/U6-RPS6KB1shRNA or rAd/U6- TP53shRNA. Twenty-4 h after the 1st transduction with the rAd/U6-shRNAs, the cells were then transduced either with rAd/CMV as control (Con), or with rAd/CMV-Arg2 or rAd/CMV-H160F to overexpress ARG2 or H160F, respectively. Experiments were performed 64 h (serum-free during the last 16 h) post the 2nd transduction. Shown are immunoblotting analyses of LC3-I/-II, ATG12–ATG5, SQSTM1, PRKAA-T172, and PRKAA, TP53-S15 and TP53, RPS6-S235/236 and RPS6, ARG2 and tubulin, which served as a loading control. Quantification of the signals is shown in the bar graphs below (n = 5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Arg2-cDNA + LacZshRNA.