Figure 1.
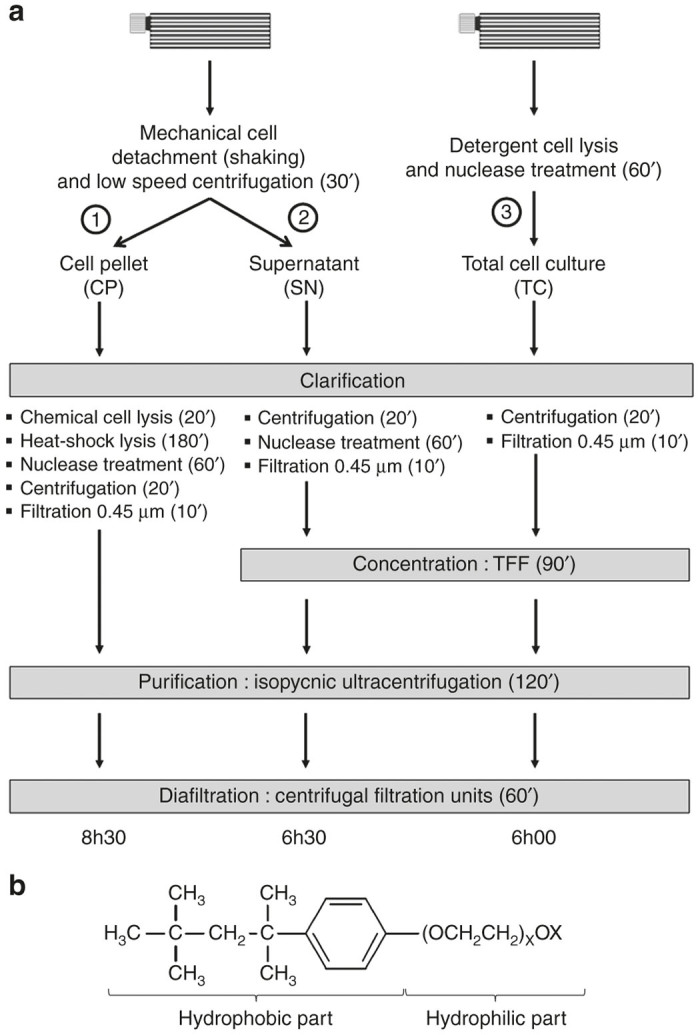
Comparison of the three different purification processes of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV). (a) rAAVs are produced in 10-layer Hyperflask vessels by using tri-transfection method in HEK293T adherent cells. In (1) and (2), cell pellet (CP) or supernatant (SN) are separated from the same Hyperflask. Adherent cells are first detached by manual flask shaking and the cell suspension is collected. The vessel is washed once with saline buffer that is pooled with the initial cell suspension. After low speed centrifugation (500 × g), to avoid cell membrane disruption, CP and SN are treated separately. In (1), cells are chemically (lysis buffer) and physically (heat-shock) lysed before enzymatic digestion of nucleic acids. Cellular debris is pelleted by high speed centrifugation (3,500 × g) and supernatant is filtrated through a 0.45 µm pore membrane. Clarified solution is deposited on iodixanol-based discontinuous density gradient and ultracentrifuged at 500,000 × g. Recovered fractions are diafiltrated and concentrated through 100 kDa molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) centrifugal filtration units. In parallel, SN (2) is first clarified by high speed centrifugation (3,500 × g) to remove cell debris. After nucleic acids digestion, a 0.45 µm filtration is performed as final clarification step. Resulting filtrate is concentrated by tangential flow filtration (TFF) using a 500 kDa MWCO hollow fiber. Concentrate is then purified and diafiltrated as described for process (1). Our new method (3) performs cell lysis by simply adding Triton X-100 detergent and nuclease directly into the Hyperflask full of its original conditioned medium. The total cell culture (TC) is collected and the vessel is washed with saline buffer. Washing solution is pooled with the initial cell suspension and centrifuged at high velocity (3,500 × g) to remove cell debris, followed by a filtration through a 0.45 µm pore membrane. The concentration, purification, and diafiltration steps are identical to those described in method (2). Each of the three purification methods differs by the process duration, and the third avoids the loss of viral particles by recovering the totality of cell culture fractions including CP and SN. (b) Structural formula of Triton X-100. This nonionic chemical detergent possesses one short hydrophobic part and one hydrophilic part consisting of a series of ethylene oxide molecules (X ~ 9 to 10). See text for more technical details.
