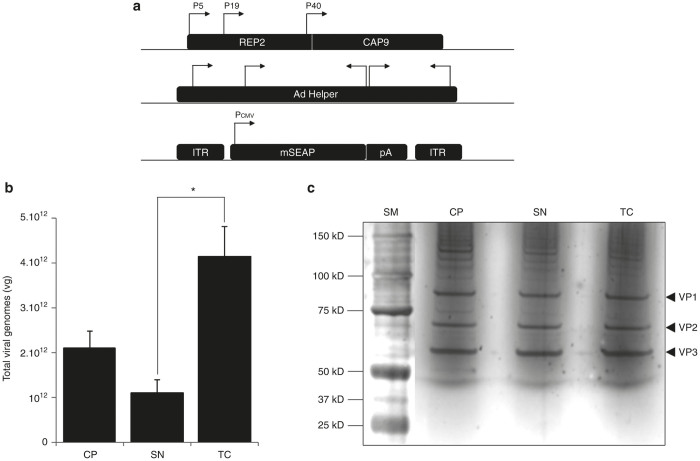
Figure 2.
Comparison of vector yields and purity between CP, SN, and TC processes. (a) Schematic representation of plasmid constructions used for recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) production. The pAAV2/9 plasmid (upper part) encodes for the rep and cap genes. Regulatory and structural AAV proteins are controlled by their natural P5 (Rep78/68), P19 (Rep52/40) and P40 (VP1, 2, and 3) promoters. The cap genes encode for serotype 9 capsid. The helper adenoviral plasmid (middle part) encodes for helper functions. The pAAV-mSEAP cis-plasmid (lower part) encodes for the mSEAP reporter gene under the control of CMV promoter (Pcmv) and terminated by a non constitutive polyadenylation site (pA). Transgene construction is cloned between two inverted terminal repeats (ITR) originating from AAV2 serotype. See Materials and Methods for more details about transfection protocol. (b) Total viral genomes (vg) recovered at the end of each type of process (CP, SN, and TC). Quantification revealed that higher rAAV recovery is achieved for TC-derived vectors, with a twofold difference between TC and CP processes (P = 0.134) and fourfold significant difference (*) between TC and SN process (P = 0.037). Refer to Materials and Methods for quantification protocol and methods of statistical analyses. Refer also to Supplementary Table S1 for titration details. (c) AAV vector quality determined by silver staining of SDS-PAGE. 1010 vg of rAAV from CP, SN, and TC processes are denatured, reduced, and migrated in 4%/12% SDS-PAGE. Silver staining of the gel reveals the three AAV capsid components materialized by 82, 67, and 60 kD bands, corresponding to VP1, VP2, and VP3 proteins respectively. Note that no other contaminating band can be distinguished on either side of the AAV capsid proteins. SM, size marker for molecular weight determination.