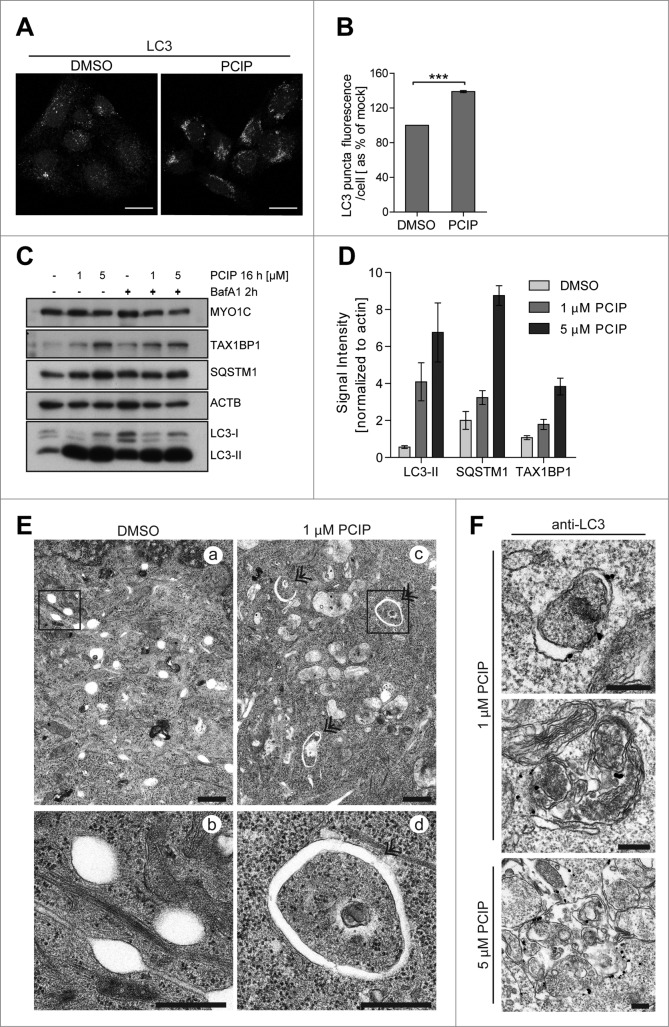
Figure 2.
(See previous page). Inhibition of MYO1C function by the small molecule inhibitor PCIP causes accumulation of LC3-positive autophagosomes. (A) HeLa cells were incubated with 2 μM of the MYO1 inhibitor PCIP or equivalent amounts of DMSO for 16 h and processed for confocal microscopy using antibodies against endogenous LC3. (B) LC3-positive vesicles in control and PClP-treated cells were quantified by high-throughput microscopy. Automated imaging and analysis software revealed a significant increase in the LC3 puncta fluorescence per cell upon PClP treatment. A total number of >41 ,000 cells from 3 independent experiments, each performed in duplicate, were analyzed. (C) Western blot analysis of HeLa cell lysates treated with PCIP for 16 h in the absence or presence of 100 nM bafilomycin A1. (D) Quantification of LC3-II, SQSTM1, and TAX1BP1 protein expression from protein gel blots of PCIP-treated HeLa cells revealed a dose-dependent increase in LC3-II, SQSTM1, and TAX1BP1 levels. Results represent the mean (+/− s.d.) from >3 independent experiments. (E) Conventional electron microscopy of HeLa cells treated with 1 μM PCIP for 16 h. Panels (b) and (d) represent enlarged boxed regions in (a) and (b). Double arrows indicate autophagosomes and phagophores. Scale bar = 500 nm. (F) HeLa cells treated with PCIP for 16 h were labeled for immuno-electron microscopy using anti-LC3 antibodies. Scale bar = 500 nm.