Figure 5.
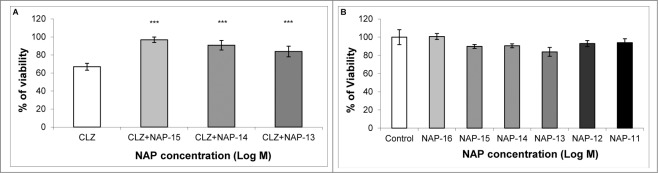
NAP protects against CLZ-associated cell death. In a neuronal cell culture model (human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma) CLZ treatment resulted in approximately 40% decreased viability (A, CLZ vs. B, control, no CLZ). NAP treatment at 10−15M to 10−13M completely protected against CLZ-related reduction in viability. (NAP+CLZ vs. CLZ, one-way ANOVA, F(3) = 103.618, P < 0.001. The Fisher Least Significant Difference (LSD) post-hoc test revealed protection by NAP concentration of 10−15M - 10−13M: ***P < 0.001), (A). In the same neuronal cell model, without the addition of CLZ, at a wide concentration range (10−16M to 10−11M), NAP did not affect cell viability or cell division (P > 0.05), (B). However, the control group in (B) shows an ‘unacceptably large variance’, thus preventing the correct assessment of NAP effect. Experiments were repeated 3 times; one representative experiment is shown (n = 5 to 10/group/experiment).
