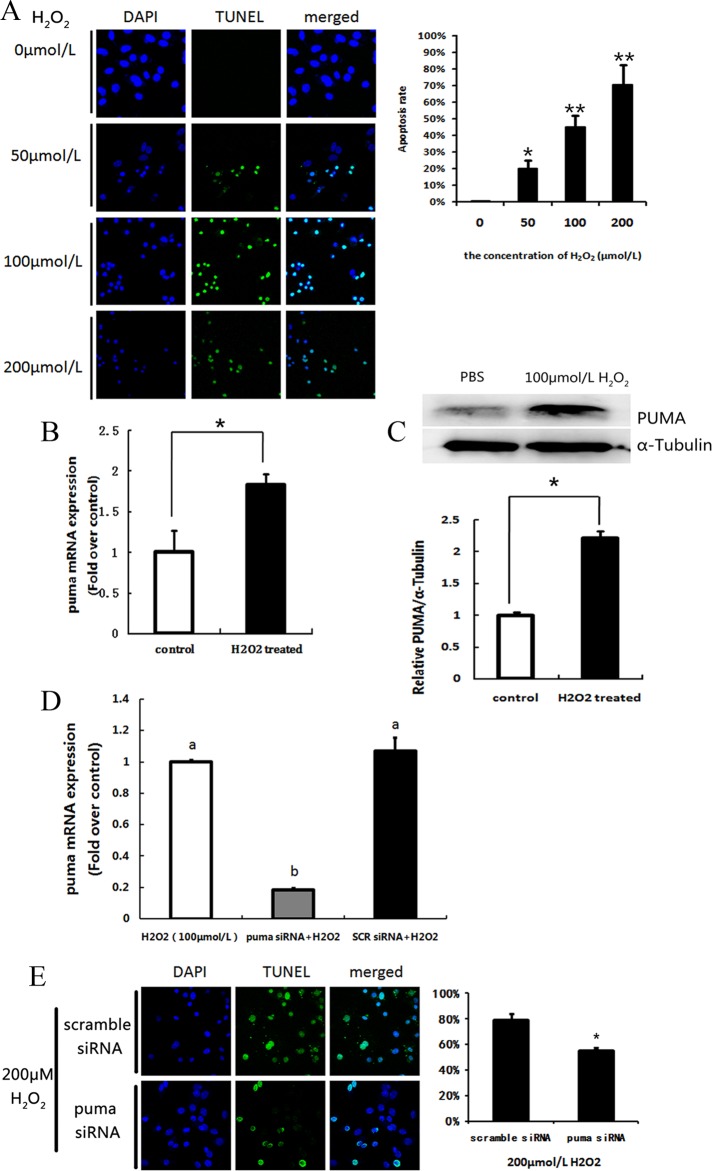
Figure 1.
Expression of p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) in cultural follicular granulosa cells (GCs) in vitro under oxidative stress. A, H2O2 dose-dependent apoptosis was detected by terminal deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining (fluorescein isothiocyanate [FITC] labeling). The TUNEL-positive cells were displayed in green staining. Nuclei were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Bar = 20 μm. The quantification of the apoptosis rates was counted in 6 independent slides. Data represent mean ± standard error. B, Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed the messenger RNA (mRNA) transcription changes of p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) in response to 100 μmol/L H2O2 treated for 24 hours in cultural follicular GCs. C, Western blot of PUMA protein level in cultural follicular GCs after treatment with 200 μmol/L H2O2 for 36 hours. An internal control was served by α-tubulin. D, Quantitative RT-PCR showed the mRNA transcription changes of PUMA in response to transfect PUMA small interfering RNA (siRNA) or scramble siRNA. E, Apoptosis rate of GCs was determined by TUNEL staining. * indicates P < .05; ** indicates P < .01.