Figure 1.
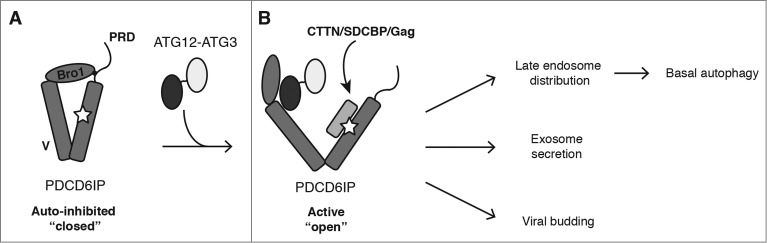
Model for ATG12–ATG3 function in PDCD6IP/Alix activation and basal autophagy. (A) Intramolecular interaction of the PRD with the Bro1 and V domains maintains PDCD6IP in an inhibitory conformation that blocks access to its YPXnL-binding site (star). (B) ATG12–ATG3 binding to PDCD6IP displaces the PRD from the Bro1 and V domains, leading to its open conformation. The accessible V domain enables recruitment of partner proteins, including CTTN (cortactin), SDCBP/syntenin and viral Gag, thereby supporting diverse PDCD6IP functions including late endosome distribution, exosome release, and viral budding. We propose basal autophagy to be dependent on the fusion of autophagosomes with late endosomes. Thus, cells lacking either PDCD6IP or ATG12–ATG3 accumulate abnormal perinuclear late endosomes that are unable to fuse with lysosomes, thereby abrogating autolysosome formation.
