Figure 2.
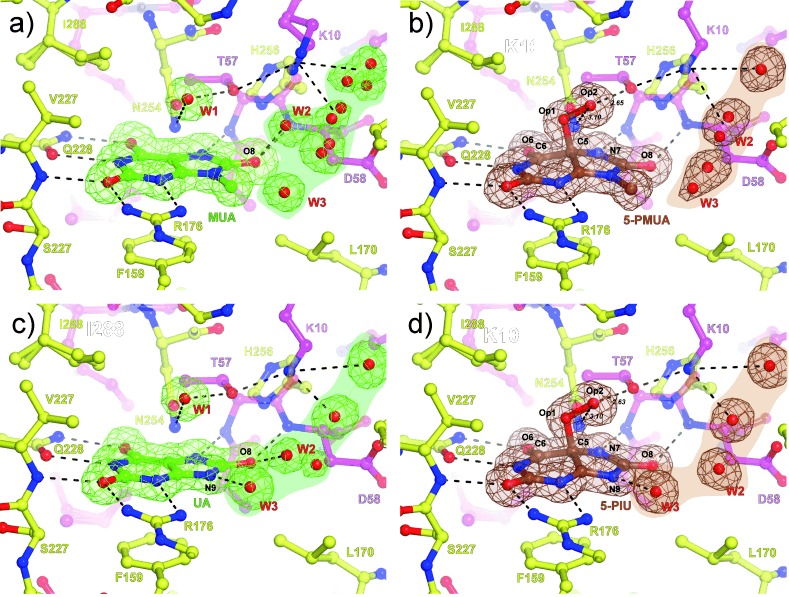
UOX-mediated catalysis proceeding via a (hydro)peroxide intermediate. a) Anaerobic UOX:MUA complex. b) UOX:5-PMUA complex. c) Anaerobic UOX:UA complex. d) UOX:5-PIU complex. UOX residues at the interface are shown in stick representation and are color-coded according to the subunit they belong to. Red spheres represent water molecules. In (a,c), 2 m Fo−D Fc electron density contoured at 1σ level is shown in green for the bound MUA and UA as well for the solvent molecules in their proximity. In (b,d), 2 m Fo−D Fc electron density contoured at 1σ level is shown in brown for the peroxides and solvent network. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines. The shaded regions highlight the solvent pool contributed by several water molecules connected by H-bonds (not shown for clarity) often exhibiting partial occupancy. In the anaerobic samples, a water molecule (W2) is H-bonded to the O8 atom of the substrate. This interaction is lost upon peroxide formation. W1 is displaced upon peroxide formation. Op1 and Op2 indicate peroxide oxygens.
