Figure 2.
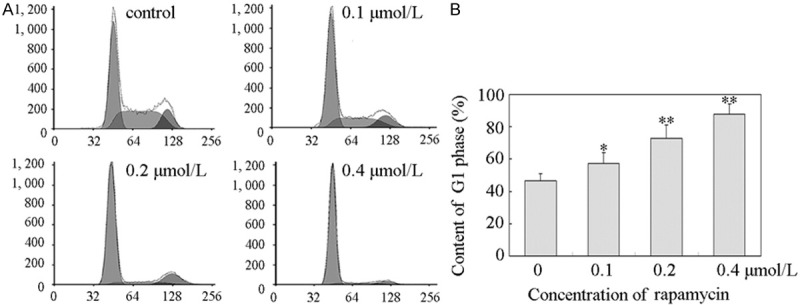
Rapamycin induced a G1 cell cycle arrest in Y79 cells. A. Rapamycin induced a G1 cell cycle arrest in Y79 cells. Y79 cells were plated in six-well culture plates and treated for 48 h with vehicle control or 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 μmol/L rapamycin for 48 h, respectively. Cell were harvested and stained with propidium iodide as described in “Materials and methods”. Nuclei were tested for DNA content by flow cytometry. All these experiments were replicated at least thrice, and a representative example of the DNA content frequency histograms was shown. B. Cell cycle distribution. Cell cycle distribution was assessed by MultiCycle AV software. The percentage of cells at G1 phase was 46.4 ± 4.5%, 57.2 ± 6.8%, 72.7 ± 8.2%, and 87.9 ± 6.2% in 0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 μmol/L rapamycin treatment, respectively. Columns, means of triplicate determinations; bars, SDs; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01 as compared with respective controls.
