Figure 2.
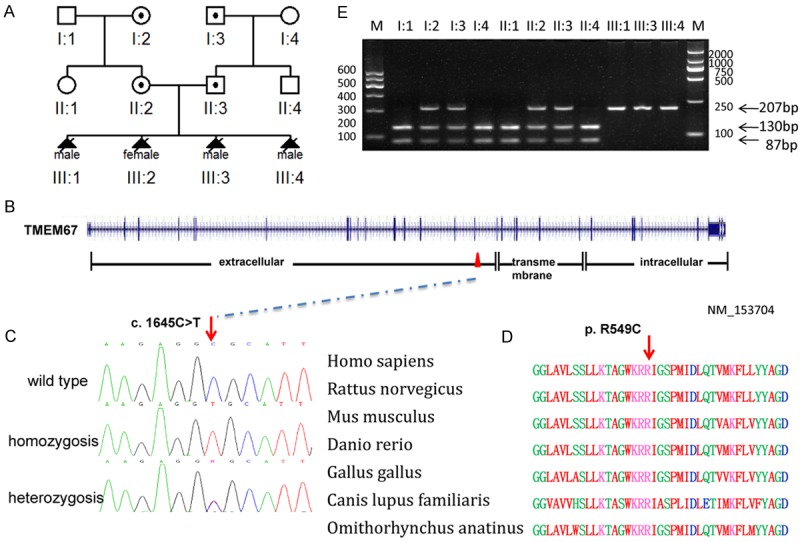
Mutation analysis of the Chinese MKS3 family. A. Pedigree of the Chinese MKS3 family. B. Genomic structure of TMEM67 (NM_153704). The 28 exons of TMEM67, encompassing 62 kb of genomic sequence, are shown as vertical bars, with their approximate sizes and positions indicated. Positions of the start codon (ATG) at nucleotide +1 and the stop codon (TAA) are indicated. Correspondence between TMEM67 exons and predicted meckelin domains is depicted at the bottom. C. Sequence chromatogram of affected individual (homozygous), carrier (heterozygous) and control (wild type). D. Conservation analysis showing that Arg549 in TMEM67 is conserved across human (Homo sapiens), rat (Rattus norvegicus), mouse (Mus musculus), zebrafish (Danio rerio), chicken (Gallus gallus), wolf (Canis lupus familiaris) and platypus, (Omithorhynchus anatinus). E. Endonuclease digestion Hha I digestion distinguish the homozygote (217 bp, III-1, III-3, III-4) from the wild-type (130, 87 bp; II-1, I-1, II-4, I-4) and heterozygote (217, 130, 87 bp; II-2, I-2, II-3, I-3) on agarose gel electrophoresis.
