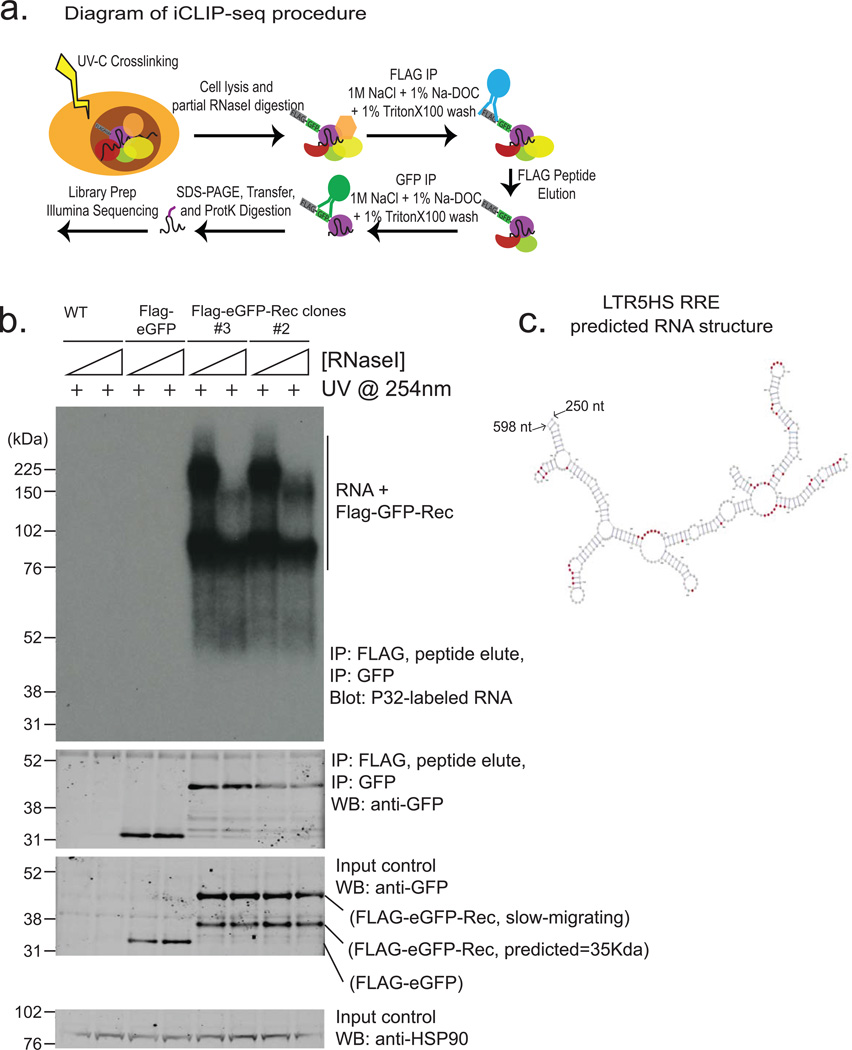
Extended Data Figure 8. iCLIP analysis of Rec-associated RNAs (supporting Fig. 4).
a) Diagram of iCLIP-seq procedure (see Methods for details). Briefly, cells are crosslinked using UV, lysed and digested with RNAse to trim RNAs. Sequential immunopurification is performed using FLAG M2, peptide elution, and GFP IP. After stringent washing, RNAs are recovered and either radiolabeld (shown in Extended Data Fig. 8b) or reverse transcribed and prepared for Illumina HTPS libraries.
b) Autoradiogram of labeled RNAs (top panel) recovered from UV-crosslinked cells using sequential Flag-eGFP IP from: wildtype hECC (lanes 1, 2), Flag-eGFP control hECC (lanes 3,4),or two independent Rec-hECC transgenic lines (lanes 5–8), separated on an SDS-PAGE gel. Free Rec protein runs as a ∼35 kDa band, while Rec protein crosslinked to RNA molecules show lower electrophoretic mobility. Please note that: i) Rec-bound RNAs are resistant to even high concentrations of RNAseI, likely indicating extensive secondary RNA structures, and (ii) low/no background of contaminating RNAs in control IP from wildtype hECCs or Flag-eGFP control hECC. Western blots with anti-GFP antibody were also performed to confirm the presence of tagged protein in Flag-eGFP control and Flag-eGFP-Rec cells, both in input and IP fractions (middle panels). HSP90 was used as a loading control (bottom panel).
c) Computationally predicted (using mFold) secondary structure of LTR5HS sequence around the Rec-response element, (identified experimentally in vitro by Lower, et al.1997). Single nucleotide resolution Rec UV-crosslinking sites determined by iCLIP are shaded in red; (n=2 biological replicates).