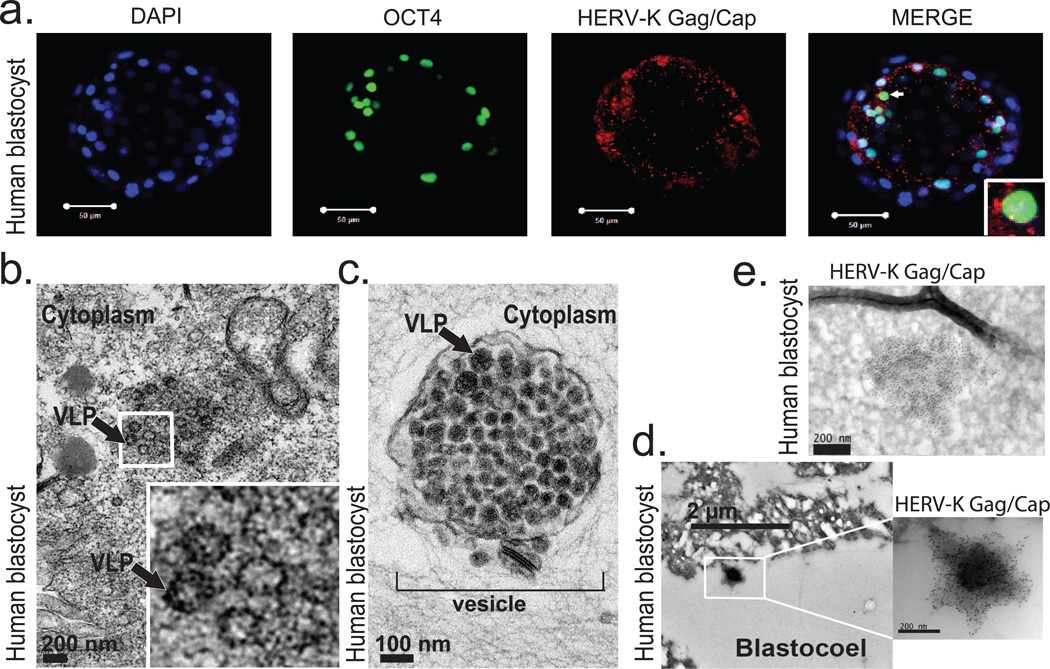
Figure 3. Human blastocysts contain HERV-K proteins and viral-like particles.
a) Immunofluorescence of human blastocysts (days post fertilization, DPF =5–6) stained with DAPI (blue), OCT4 antibody (green), and HERV-K Gag/Capsid antibody (Red). Images show a representative example (n=19 embryos). Scale bar = 50 microns, 1 micron confocoal z-slice. White arrow points to an OCT4+ cell, surrounded by cytoplasmic Gag/Capsid, which is shown with higher magnification in an inset.
b) Heavy metal staining transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of human blastocyst, arrow denotes putative VLP (found in n=2/3 blastocysts, DPF=5–6). Higher magnification of indicated region shown in inset. Scale bar = 200nm.
c) Heavy metal staining TEM of human blastocyst, arrow denotes putative immature VLP, bracket indicates vesicle filled with putative VLP, (found in n=2/3 blastocysts, DPF=5–6). Scale bar = 100 nm.
d-e) Immuno-TEM of human blastocysts with Gag/Capsid staining, region of higher magnification is boxed. Representative examples of budding (d) and cell-internal (e) particles are shown; n =3 blastocysts (DPF=5–6), n=3 labeled particles in 2 embryos.