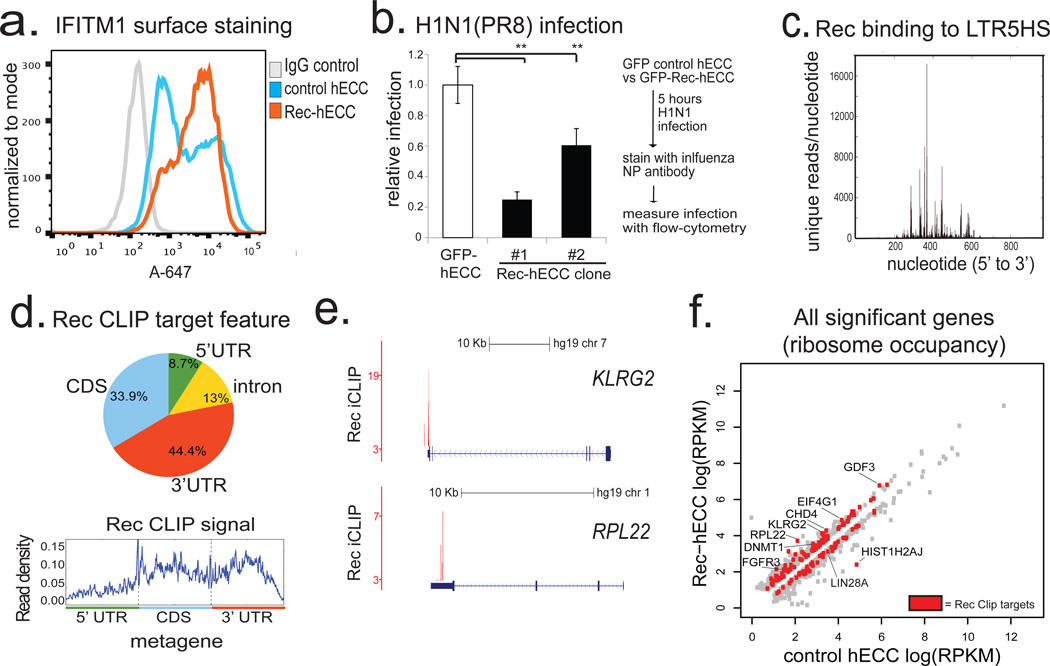
Figure 4. HERV-K accessory protein Rec upregulates viral restriction pathway and engages cellular mRNAs.
a) Flow cytometry histograms of IFITM1 surface staining in control hECC or Rec-hECC (NCCIT) cells, histogram of negative control cells stained with isotype IgG+Alexa-647 secondary is shown for comparison. Shown is a representative result of two independent experiments.
b) H1N1(PR8) influenza infection of control GFP-hECC cells or two clonal lines of Rec-hECC (NCCIT). Control cells were set as 100%, shown is aggregate results from 2 independent experiments, n=8 total biological replicates for each condition. Error bars are +/− 1 S.D. ** denotes p-value <0.005, one-sided t-test.
c) Rec iCLIP reads mapped to the LTR5HS sequence, n= 2 biological replicates.
d) Distribution of Rec binding sites on endogenous mRNAs (top) and aggregate Rec iCLIP-seq signal on a metagene (bottom), n=2 biological replicates.
e) Distribution of Rec iCLIP reads at representative target mRNAs KLRG2 (top), RPL22 (bottom); y-axis, iCLIP score, at cut-off = 3 (see Methods for details)
f) Ribosome profiling signal for all significant genes (FDR<0.05 Cuffdiff) in wildtype hECC cells vs Rec-hECC (NCCIT), n=4 biological replicates. Rec iCLIP targets are colored in red