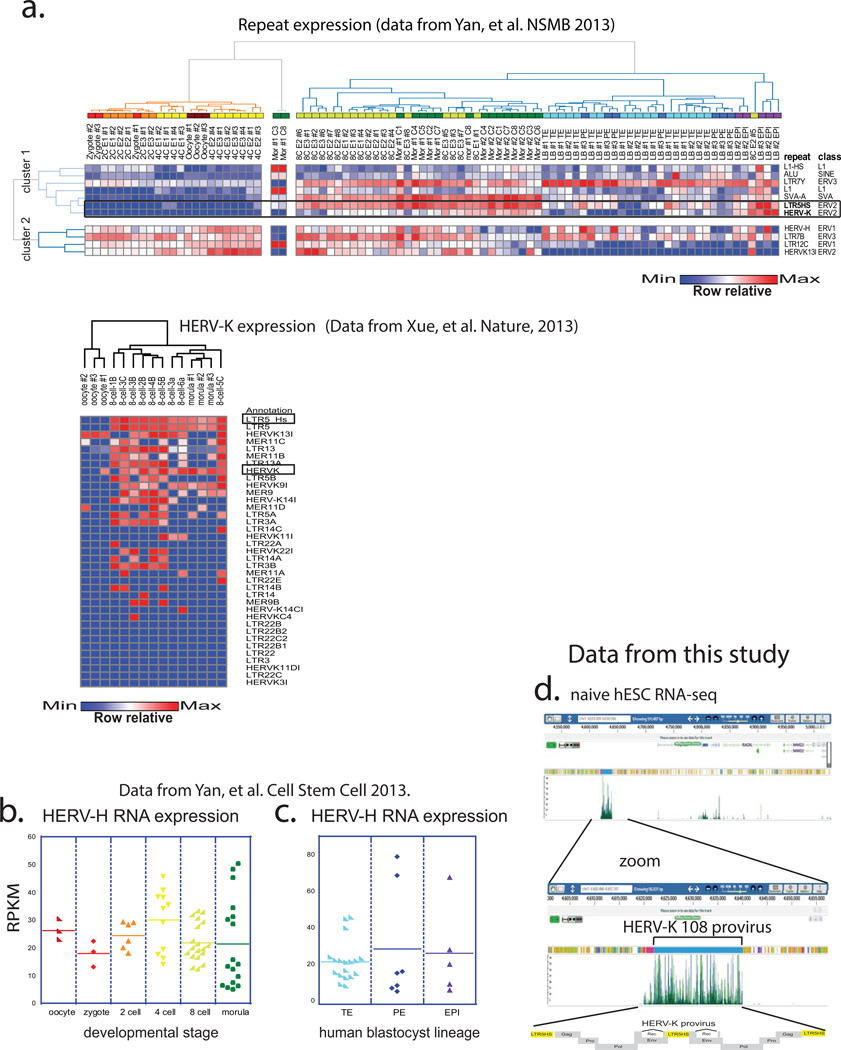
Extended Data Figure 1. Additional single-cell RNA-seq data analyses from pre-implantation human embryos (supporting Fig.1).
a) Heat map and hierarchical K-means clustering of highly expressed (average RPKM>6 across 89 embryo libraries) repetitive elements in single cells of human preimplantation embryos at indicated developmental stages (top) and HERV-K expression (bottom) using indicated datasets.
b) HERV-H expression (RPKM) in single cells of human embryos at indicated preimplantation stages. Solid line = mean. RNA-seq from Yan, et al. 2013.
c) HERV-H expression (RPKM) in single cells of human blastocysts, grouped by lineage, solid line = mean. Oocyte (n=3), zygote (n=3), 2C (n=6), 4C (n=11), 8C (n=19), mor (n=16), TE (n=18), PE (n=7), EPI (n=5), p0 (n=8), p10 (n=26). RNA-seq dataset was from Yan, et al. 2013.
d) Genome browser snap-shot showing 100bp-PE-RNA-seq reads from ELF1 naïve hESC cells aligning at the HERV-K 108 provirus on chromsome 7.