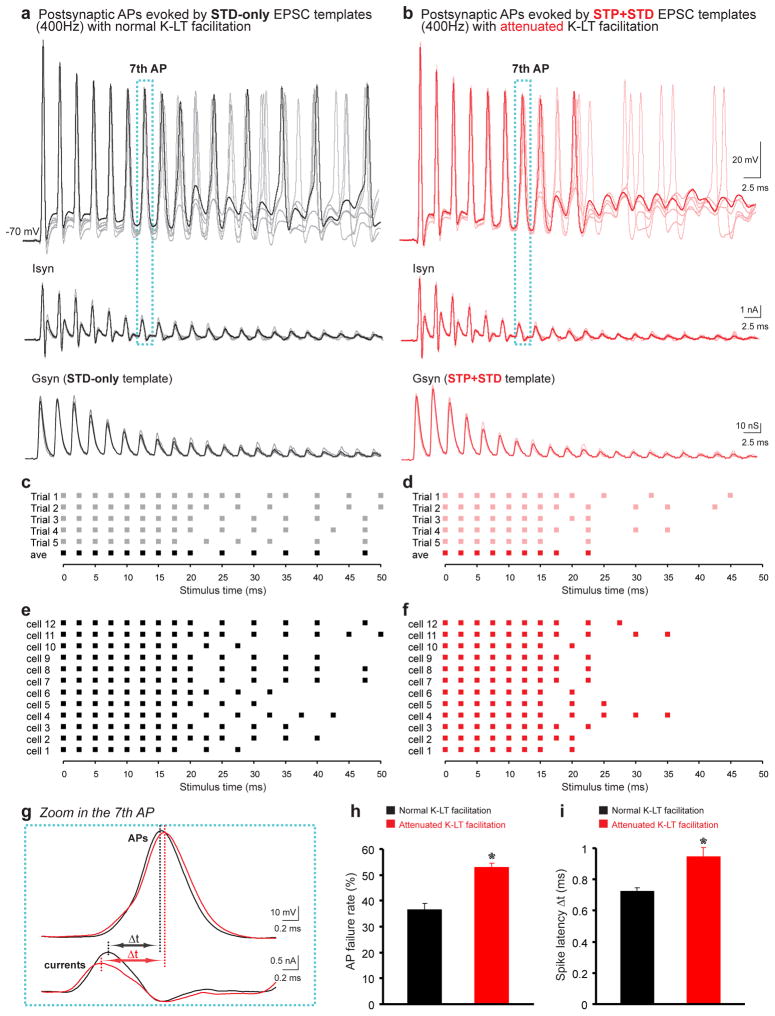
Figure 8. Indispensable role of Kv facilitation in boosting spiking fidelity of principal neurons.
(a & b) Conductance templates (Gsyn), STD-only (individual trials in grey and average trial in black, a) and STP+STD (individual trials in pink and average trial in red, b), are generated by reversing the polarity of two sets of representative recordings of Post-IEPSC respectively evoked by the train stimulation (400 Hz) with normal or attenuated IK-LT facilitation (bottom panels). Spikes evoked by stimulation currents (Isyn, middle panels) in the dynamic-clamp configuration by injecting the EPSC templates into the same postsynaptic neurons are shown in top panels. (c & d) APs produced by the five individual and average conductance templates for each group are summarized. Each square represents a spike. (e & f) Raster plots of APs generated by the average conductances of five repeats against stimulus time in 12 cells. (g) Time difference between the peak of the 7th stimulation currents and that of their resulting APs during the train stimuli, termed as spike latency, is illustrated to display the prolonged spike latency without IK-LT facilitation. (h & i) Failure rate (h) and latency (i) of spikes produced by the STD-only (black bars) or STP+STD template (red bars) are compared (n=12). The asterisks indicate statistical significance (p<0.0001 in both cases, two-tailed paired Student’s t-tests). Error bars denote ± s.e.m.