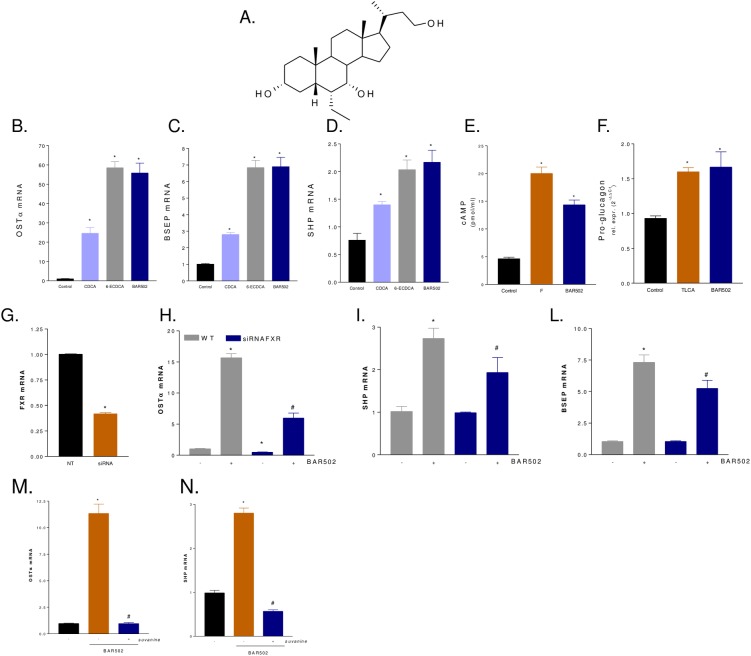
Fig 1. In vitro pharmacological characterization of BAR502.
(A) Chemical structure of BAR502. (B-D) Serum starved HepG2 cells were stimulated 18 h with 10 M CDCA, 6-ECDCA or BAR501 and the relative mRNA expression of OSTα (B), BSEP (C) and SHP (D) was assayed by RT-PCR. Results are the mean ± SE of three experiments. *p<0.05 versus not treated cells (NT). (E) Serum starved THP-1 cells were stimulated with BAR501 or forskolin as indicated in materials and methods. At the end of stimulation intracellular cAMP levels were measured. (F) Glutag cells were stimulated 18 h with 10 M TLCA or BAR501 and the relative mRNA expression of pro-glucagon was assayed by RT-PCR. Results are the mean ± SE of three experiments. *p<0.05 versus not treated cells (NT). (G-L) Effect of FXR silencing on activity of BAR502 on FXR target genes. HepG2 cells were left untransfected or transfected with a cocktail of four siRNA directed against FXR. 48 hours post transfection cells were stimulated 18 with BAR502 (10 M) and the relative mRNA expression of FXR (G), OSTα (H), SHP (I) and BSEP (L) were assayed by RT-PCR. (M-N) Effect of FXR antagonism by suvanine. Serum starved HepG2 cells were stimulated 18 hours with BAR502 (10 M) or with the combination of BAR 502 plus suvanine (50 M). At the end of stimulation the relative mRNA expression of OSTα (M) and SHP (N) were assayed by RT-PCR.