Figure 2. Weak Ras mutants in mammalian cells can behave as strong activators of Ras pathway signaling under the Nf1 deficient conditions.
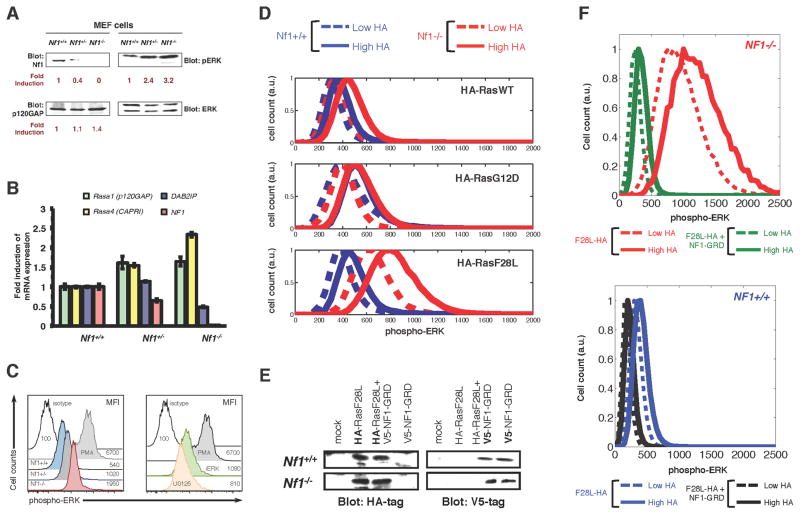
(A) Immunoblots of Nf1+/+, Nf1+/−, and Nf1−/− mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) for expression of neurofibromin, p120 Ras GAP, and phosphorylated ERK.
(B) MEFs of the Nf1+/+, Nf1+/−, and Nf1−/− genotype were analyzed by qPCR for Ras GAP genes Rasa1 (p120GAP), Rasa4 (CAPRI), DAB2IP, and Nf1. Error bars represent standard deviation from three independent experiments from three different RNA extractions/preparations.
(C) (left) Histograms present p-ERK profiles within Nf1+/+, Nf1+/−, and Nf1−/− MEF cells. Data presented are representative of at least 6 similar experiments. (right)
(D) Nf1+/+ and Nf1−/− MEFs transfected with HA-tagged H-RasWT, H-RasF28L, or H-RasG12D with HA-tag expression and pERK signal quantified by multi-color flow cytometry.
(E) Immunoblots showing expression of HA-tagged H-RasF28L and V5-tagged NF1-GRD in Nf1−/− and Nf1+/+ MEF cells following transfection, either alone or together.
(F) MEFs transfected with HA-tagged H-RasF28L or with HA-tagged H-RasF28L and NF1-GRD with HA-tag expression and pERK signal quantified by multi-color flow cytometry.. Nf1(−/−) + F28L, red; Nf1(−/−) + F28L + NF1-GRD, green; Nf1(+/+) + F28L, blue; Nf1(+/+) + F28L + NF1-GRD, black. Higher HA, solid; lower HA, dashed.