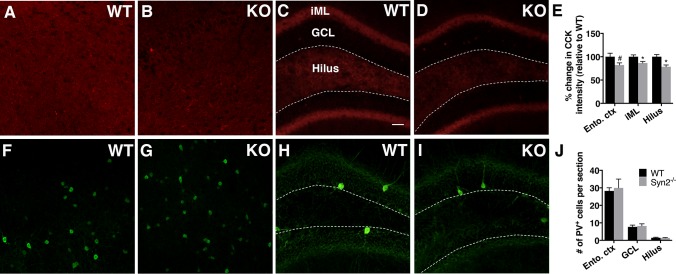
Fig 5. Reduced cholecystokinin (CCK) inhibitory presynaptic input in epileptogenic 1-month old Syn2-/- mice.
Representative images showing CCK immunoreactivity in entorhinal cortex and hippocampus in WT (A and C) and Syn2-/- (KO) (B and D) mice. Note a strong immunoreactive band in the inner molecular layer (iML) of dentate gyrus (C and D). Quantification of percentage change in CCK intensity relative to WT in entorhinal cortex (ento. ctx), iML and dentate hilus (E). Images showing parvalbumin (PV) immunoreactivity in entorhinal cortex and hippocampus in WT (F and H) and Syn2-/- (G and I) mice. Quantification of mean number of PV+ cells per brain section in entorhinal cortex, granule cell layer (GCL) and dentate hilus (J). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 7 WT and 8 Syn2-/-. *, p ≤ 0.05, #, p = 0.059, unpaired t test. Scale bar is 40 μm (in C for A-D and F-I).