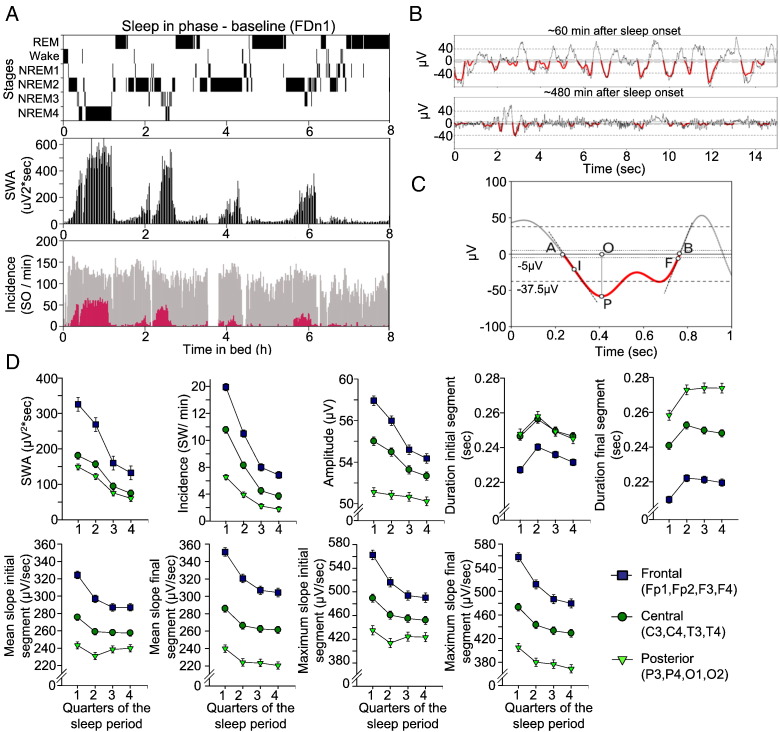
Fig. 2.
Baseline sleep and SW detection.
A. Time course of sleep stages during the participant's (BB0214, Female) baseline night (FDn1) (upper panel), the time course of slow wave activity (SWA: 0.5–4.0 Hz) (middle panel) and the incidence of the individually detected slow waves (SWs) (bottom panel). The grey bars represent all the SWs > 5 μV. The red bars represent the SOs > 37.5 μV. Artefact segments appear as gaps in activity.
B. A representative 15-second example of NREM sleep during baseline sleep (FDn1) of the same participant at ~ 1 h (upper panel) and at ~ 8 h after sleep onset, respectively. The thin black line represents the original raw EEG signal, the bold red lines indicate negative half-waves of EEG signals filtered between 0.5 and 4.0 Hz (see Materials and methods).
C. Schematic representation of detection of SWs and extraction of relevant properties from a single half-wave in a 0.5–4Hz band-pass filtered signal. The negative half-wave enclosed between zero crossings A and B has its main peak (P) at time O. The dotted line tangential to the wave in I has the steepest slope (maximum slope) in the initial (AO) phase, while the one tangential to the wave in F has the steepest slope in the final (OB) phase. Mean initial and final slopes are calculated as the ratios PO/OA and PO/BO, respectively. The numbers of peaks, two in the example given, are also counted. The dashed lines indicate the ± 5 μV and ± 37.5 μV voltage threshold levels used as amplitude criteria for detecting SWs.
D. The effect of time in bed (quarter of sleep period) and brain topography on SWA in NREM sleep and the raw SW measures during the first 8 h of baseline sleep (FDn1). The results for negative half-waves are presented. Least square (Ls) means (absolute values) and standard error of the mean (SEM) derived from the mixed model analyses are indicated for all studied sleep intervals (2 hourly bins) and main brain regions. The brain topography factor comprises three main brain regions each including weighted averages over the Frontal (Fp1, Fp2, F3, F4), Central (C3, C4, T3, T4), and Posterior (P3, P4, O1, O2) areas. The three brain derivations are indicated with different circles (Frontal derivation = dark blue square; Central derivation = dark green circle; Posterior derivation = light green triangle). For statistical results of the SW parameters please refer to Table 1.