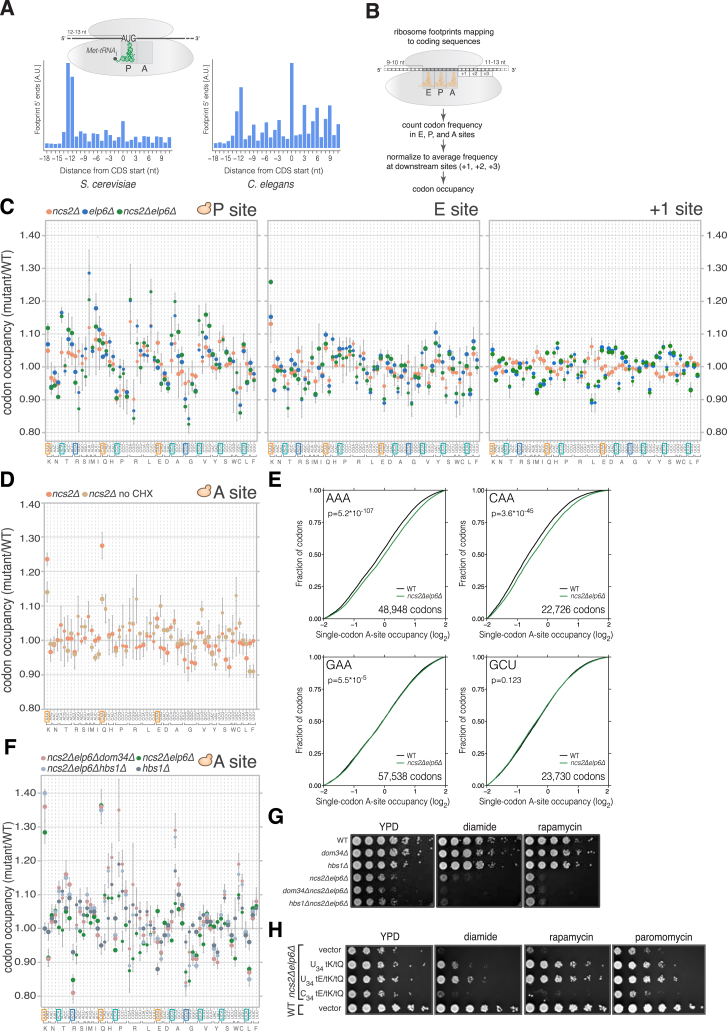
Figure S1.
Effects of U34 Modification Loss on Ribosome Occupancy at Codons Flanking the A Site In Vivo, Related to Figure 1
(A) Cumulative coverage of 5′ nucleotides from ribosome footprint reads mapping near start codons across all transcripts in S. cerevisiae (left) and C. elegans (right). Reads of length between 29 and 31 nucleotides (nt) mapped without mismatches are shown. The peak located 12-13 nt upstream of start sites is inferred to represent ribosomes poised for translation initiation that contain the AUG codon in their P-site.
(B) Approach for determining codon representation in tRNA-binding sites within ribosome footprints inferred from (A).
(C) Codon occupancy within P, E, and +1 sites in yeast with U34 modification defects compared to WT (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(D) Codon-specific changes in A-site ribosome occupancy in ncs2Δ cells compared to WT when cycloheximide (CHX) was omitted from all steps of the ribosome profiling protocol (mean ± SD; n = 3). Data from CHX-treated ncs2Δ cells is from Figure 1B.
(E) Cumulative distribution of A-site ribosome occupancy at individual AAA, CAA, GAA, and GCU codons in WT and ncs2Δelp6Δ yeast. To calculate single-codon occupancy, data from three biological replicates were pooled, and the number of A-site reads at a particular codon was normalized to the average per-codon A-site read density in the ORF containing it (p values are from a one-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test).
(F) Codon-specific changes in A-site ribosome occupancy in S. cerevisiae strains lacking U34 modifications and ribosome rescue factors (mean ± SD; n = 3). Note that the elevated occupancy at codons such as CCG and CGC in dom34Δncs2Δelp6Δ and hbs1Δncs2Δelp6Δ cells is likely caused by additive effects, as occupancy at these codons is increased in hbs1Δ yeast.
(G) Exponentially growing cultures from the indicated strains were serially diluted and spotted on medium without additives (YPD) or containing 1.2 mM diamide or 1.9 nM rapamycin. Plates were imaged after 2 days of incubation at 30°C.
(H) Cultures from the indicated strains carrying an empty vector or overexpressing isoacceptors for E, K, and Q with U34 (tEUUC, tKUUU, and tQUUG) or C34 (tECUC, tKCUU, and tQCUG) were grown to exponential phase, serially diluted, and spotted on the indicated plates. Images were taken after 2 days of incubation at 30°C.