FIGURE 1.
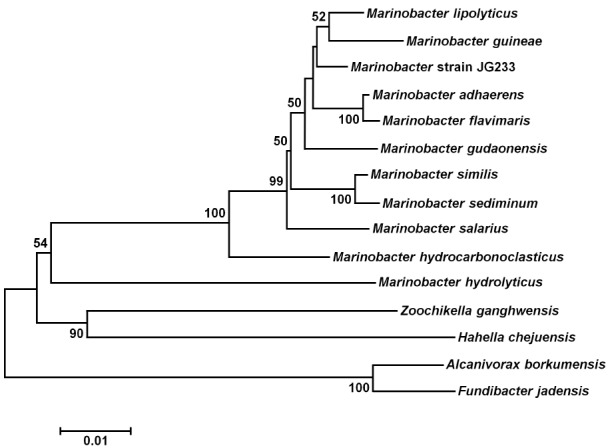
Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic tree of the 16S rRNA gene placing Marinobacter subterrani JG233 in the genus Marinobacter. Evolutionary relatedness was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987) based on the Jukes-Cantor method (Jukes and Cantor, 1969). Branch lengths are measured in the number of substitutions per site. Sequences were obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information, and were trimmed to as to attain a total of 1417 positions in the final dataset representing similar regions of the 16S rRNA gene. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6 (Tamura et al., 2013). Accession numbers for included species are as follows: Marinobacter adhaerens (NR_074765), Marinobacter similis (KJ547704), Marinobacter gudaonensis (NR_043796), Marinobacter salarius (KJ547705), Marinobacter lypolyticus (NR_025671), Marinobacter flavimaris (NR_025799), Marinobacter sediminum (NR_029028), Marinobacter guineae (NR_042618), Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus (NR_074619), Zooshikella ganghwensis (AY130994), Microbulbifer hydrolyticus (AJ608704), Alcanivorax borkumensis (Y12579), Fundibacter jadensis (AJ001150), and Hahella chejuensis (AF195410).
