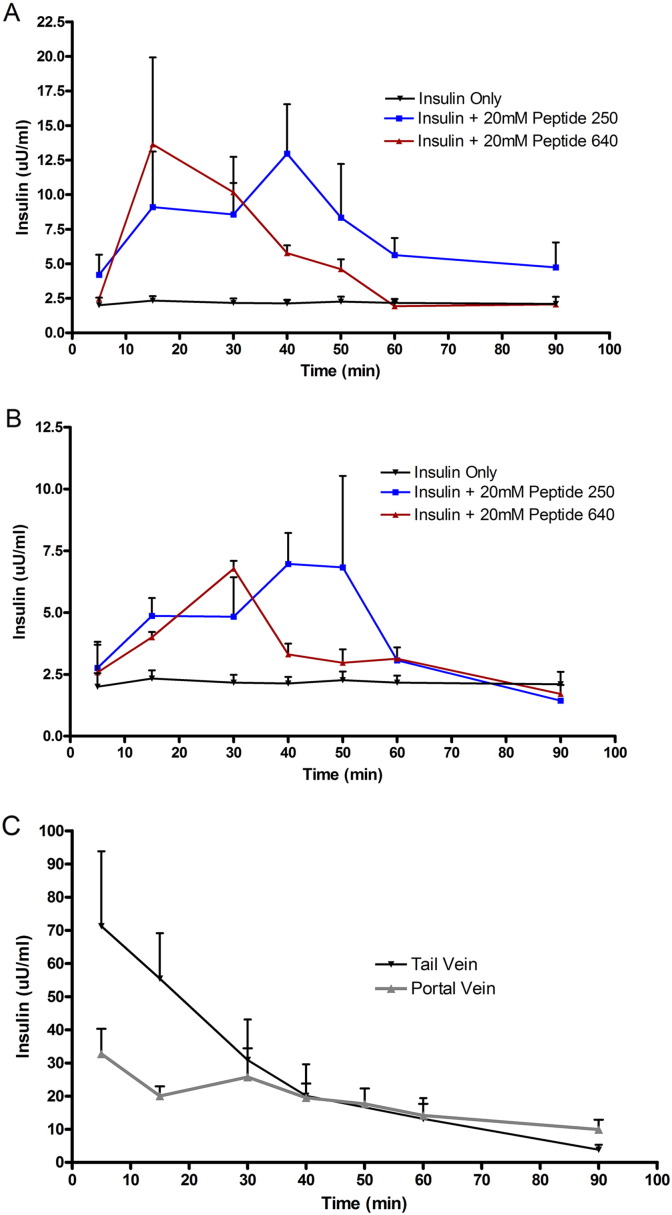
Fig. 5.
PIP peptides 250 and 640 enhance the uptake of human insulin with different kinetics from the intestinal lumen of non-diabetic rats. (A) Time-concentration profiles of insulin in serum samples from blood collected from the portal vein following ILI injection of PIP peptides with 30 IU/kg of insulin. One-way ANOVA shows data sets are significantly different from each other (p < 0.01). Bonferroni post-tests show that insulin with peptide 250 (p < 0.01) and insulin with peptide 640 (p < 0.05) were significantly different from insulin only. (B) Time-concentration profiles of insulin in serum samples collected from the tail vein following ILI injection of PIP peptides with 30 IU/kg of insulin. There was no significant difference between the groups when compared using one way ANOVA (C) Time-concentration profiles of insulin in in serum samples of blood collected from the tail and portal veins of non-diabetic mice following a SC injection of 3 IU/kg of human insulin. Data are means ± SD for n = 3 for each treatment group.