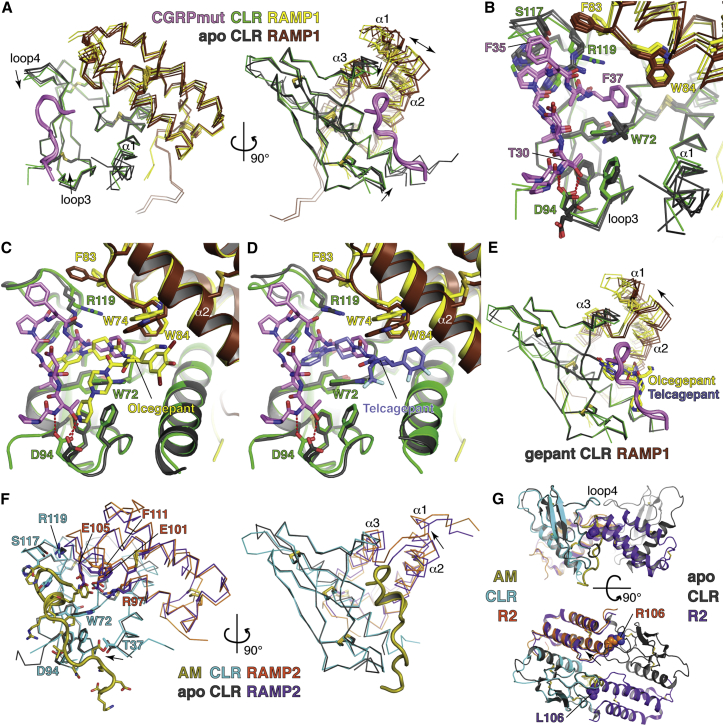
Figure 3.
Comparisons of the CGRPmut- and AM-Bound Structures to Ligand-free and Small Molecule Antagonist-Bound Structures
(A) CGRPmut-bound complexes from Mol A and Mol C were aligned with four independent ligand-free CLR:RAMP1 complexes (PDB: 3N7P) based on the CLR positions. Mol B of the CGRPmut-bound structure was omitted because crystal packing altered its conformation. Receptors are shown as Cα traces. Arrows denote the directions of loop movements upon CGRPmut binding. The double-headed arrow highlights variability in the RAMP1 position relative to CLR.
(B) Detailed view of differences between the CGRPmut-bound and ligand-free states of the CLR:RAMP1 ECD complex. CGRPmut F27 and V28 are omitted for clarity.
(C and D) Superposition of CGRPmut-bound and olcegepant-bound (PDB: 3N7S) (C) or telcagepant-bound (PDB: 3N7R) (D) structures aligned based on the CLR positions. The peptide and small molecules are shown as sticks.
(E) Superpositions of the CGRPmut-bound structures with two independent olcegepant-bound complexes and a single telcagepant-bound complex based on the CLR positions. The arrow indicates the direction of movement of RAMP1 from the small molecule antagonist-bound to CGRPmut-bound states.
(F) Superposition of the AM-bound and ligand-free (PDB: 3AQF) CLR:RAMP2 ECD structures aligned based on the CLR positions. Receptors are shown as Cα traces and selected receptor and peptide residues as sticks. Arrows indicate directions of movement from ligand-free to AM-bound states.
(G) Putative dimer of ligand-free CLR:RAMP2 ECD heterodimers with the AM-bound CLR:RAMP2 ECD [L106R] heterodimer superimposed based on the CLR positions. The receptors and peptide are in cartoon representation and residues L/R106 are in space-filling representation. The arrow indicates the shift of RAMP2 in the AM-bound structure as compared to the ligand-free state. The top image is oriented similar to that in (F), right image.