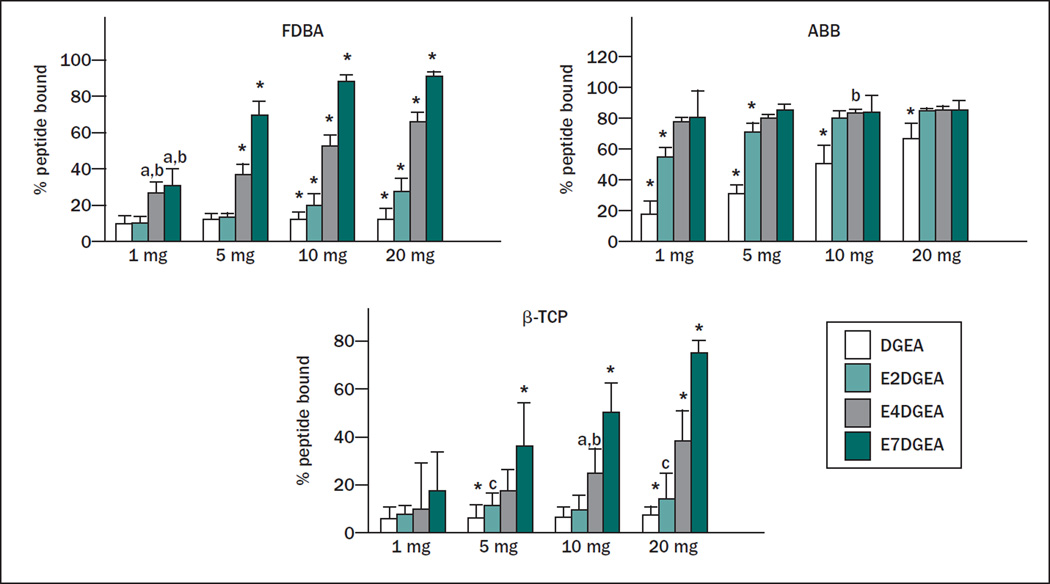
Fig 2.
Increasing length of glutamate domain confers greater peptide binding to three distinct bone grafts. Varying quantities of FDBA, ABB, or β-TCP (1 to 20 mg) were coated for 30 minutes with DGEA, E2DGEA, E4DGEA, or E7DGEA (all tagged with FITC). After the binding interval, the solution was collected and fluorescence measured via fluorometer. The percent of peptide bound was calculated by subtracting the residual fluorescence (representing unbound peptide) from the starting solution fluorescence (representing total amount of peptide added). Results show that increasing the length of the glutamate domain increases the amount of peptide bound to the three grafts tested. Significant difference (P < .05) between samples was denoted as follows: relative to DGEA = a, E2DGEA = b, E4DGEA = c, E7DGEA = d, and * to all.