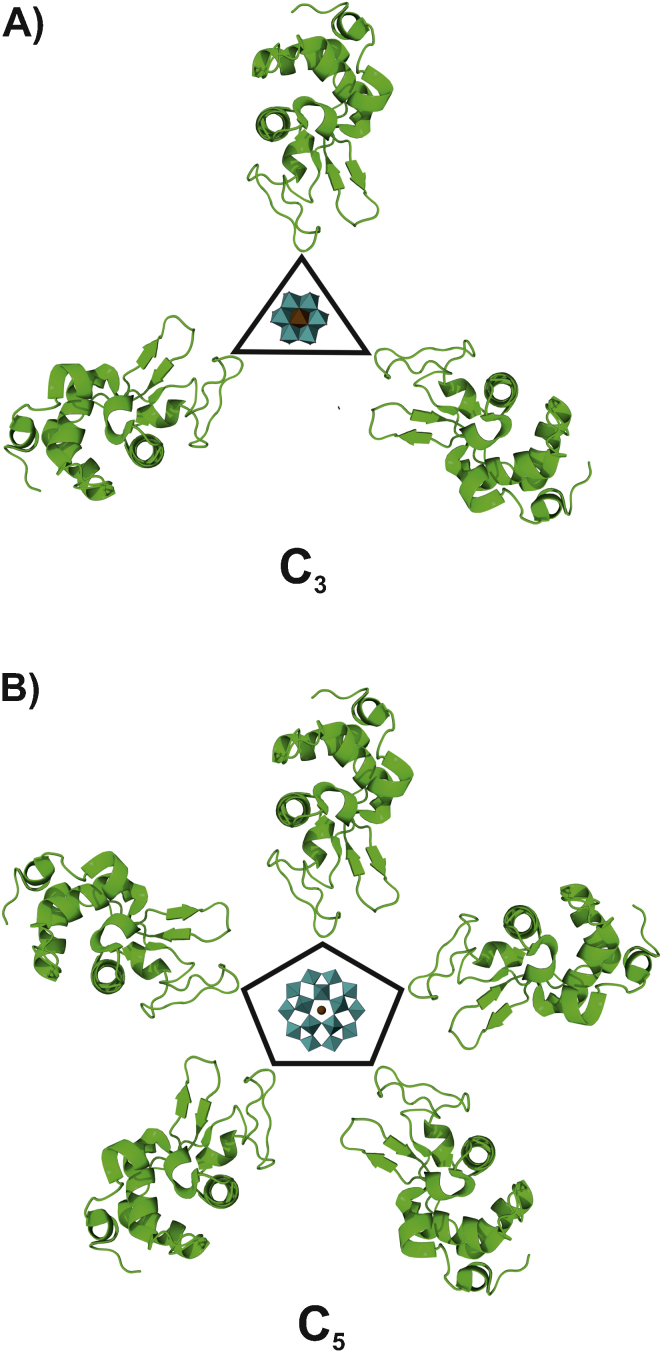
Fig. 9.
Symmetry influencing the degree of POM crosslinking. (A) An Anderson–Evans type POM ([TeW6O24]6−) is located on a crystallographic threefold axis and thus interacts with three protein monomers. The POM is shown in polyhedra representation (color code: tellurium atom = brown, tungsten atoms = cyan). The proteins are depicted as green cartoons (hen egg white lysozyme is used as an example). (B) The Preyssler type POM ([NaP5W30O110]14−) with a pentagonal symmetry is sitting on a crystallographic fivefold axis and is thus able to interact with five symmetry related protein monomers. The POM is shown in polyhedra representation (color code: sodium atom = brown, tungsten atoms = cyan). The proteins are depicted as green cartoons (hen egg white lysozyme is used as example).