Fig. 1.
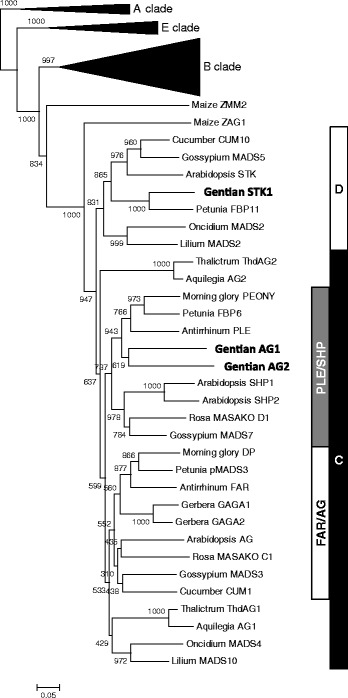
Phylogenetic tree of C/D-class MADS-box proteins. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method using ClustalW and visualized using MEGA6. Genbank accession numbers of amino acid sequences used in phylogenetic analysis are as follows: Arabidopsis thaliana AG (NP_567569), SHP1 (NP_001190130), SHP2 (NP_850377) and STK (NP_192734); Antirrhinum majus FAR (CAB42988) and PLE (AAB25101); Aquilegia alpina AG1(AAS45699) and AG2 (AAS45698); Cucumis sativus CUM1 (AAC08528) and CUM10 (AAC08529); Gentiana scabra GsAG1 and GsAG2 (this study); Gerbera hybrida GAGA1 (CAA08800) and GAGA2 (CAA08801); Gossypium hirsutum MADS3 (AAL92522), MADS5 (ABM69043) and MADS7 (ABM69045); Ipomoea nil DP (BAC97837) and PEONY (BAC97838); Lilium longiflorum MADS2 (AAS01766) and MADS10 (AIJ29174); Oncidium hybrida MADS2 (AIJ29175) and MADS4 (AIJ29176); Petunia hybrida FBP6 (CAA48635), FBP11 (CAA57445), PFG (AAF19721) and pMADS3 (Q40885); Rosa rugosa MASAKO C1 (BAA90744) and MADSKO D1 (BAA90743); Thalictrum dioicum ThdAG1 (AAS45683) and ThdAG2 (AAS45682); Zea mays ZAG1 (AAA02933) and ZMM2 (NP_001104926). Numerals beside branches indicate bootstrap values from 1,000 replicates. Scale bar indicates 0.05 amino acid substitutions per site
