Figure 1.
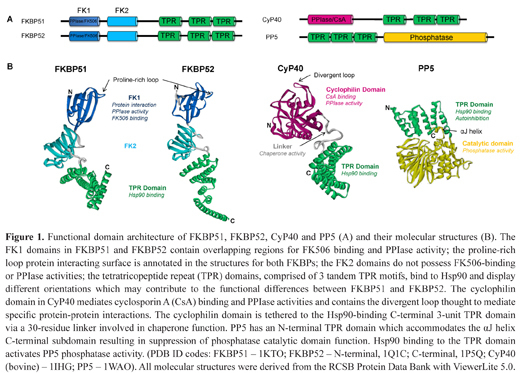
Functional domain architecture of FKBP51, FKBP52, CyP40 and PP5 (A) and their molecular structures (B). The FK1 domains in FKBP51 and FKBP52 contain overlapping regions for FK506 binding and PPIase activity; the proline-rich loop protein interacting surface is annotated in the structures for both FKBPs; the FK2 domains do not possess FK506-binding or PPIase activities; the tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domains, comprised of 3 tandem TPR motifs, bind to Hsp90 and display different orientations which may contribute to the functional differences between FKBP51 and FKBP52. The cyclophilin domain in CyP40 mediates cyclosporin A (CsA) binding and PPIase activities and contains the divergent loop thought to mediate specific protein-protein interactions. The cyclophilin domain is tethered to the Hsp90-binding C-terminal 3-unit TPR domain via a 30-residue linker involved in chaperone function. PP5 has an N-terminal TPR domain which accommodates the αJ helix C-terminal subdomain resulting in suppression of phosphatase catalytic domain function. Hsp90 binding to the TPR domain activates PP5 phosphatase activity. (PDB ID codes: FKBP51 – 1KTO; FKBP52 – N-terminal, 1Q1C; C-terminal, 1P5Q; CyP40 (bovine) – 1IHG; PP5 – 1WAO). All molecular structures were derived from the RCSB Protein Data Bank with ViewerLite 5.0.
