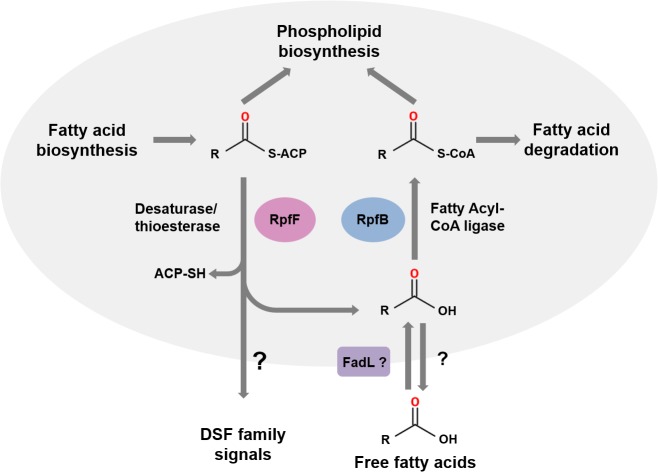
Fig 2. The roles of RpfF and RpfB in DSF signaling.
RpfF encodes an enzyme from the crotonase family that possesses both desaturase and thioesterase activities and uses fatty acyl ACP substrates derived from fatty acid biosynthesis as substrates. DSF family signals are generated from 3-hydroxy-fatty acyl ACPs by consecutive or coordinated desaturase and thioesterase action. In addition, the thioesterase activity of RpfF generates a range of free hydroxylated and non-hydroxylated fatty acids. DSF family signals leave the cell by as-yet-unknown efflux mechanisms (indicated by the question mark). Free fatty acids whose synthesis depends upon RpfF can also be found in the culture supernatant. The role of RpfB is in mobilization of these free fatty acids. Uptake, which may involve FadL, is followed by conversion to fatty acyl CoA derivatives that can be used in phospholipid biosynthesis or for degradation. This figure is a modified version of that published by Bi and colleagues [15].