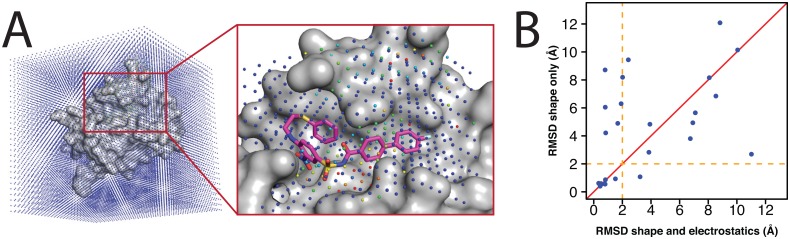
Fig 5. Incorporation of electrostatic complementarity into DARC 2.0.
(A) The electrostatic potential is evaluated at a series of grid points over the whole protein using the finite difference Poisson-Boltzmann solver included in OpenEye’s ZAP toolkit [45]. We use trilinear interpolation of the closest gridpoints to determine the electrostatic potential at points corresponding to locations of ligand atoms, and then use the ligand partial charges to compute the electrostatic interaction energy (Eq 3). (B) For each protein-ligand complex in our set (S1 Table), we used DARC to dock the ligand back into its cognate receptor either with or without including the electrostatic complementarity term. In both cases, leave-one-out cross-validation was used to ensure the weights were not overfit to the training set. Each point represents a separate complex; points above the diagonal are those for which inclusion of electrostatics led to better pose recapitulation.