Fig 1. Structural features of the TmCorA protein.
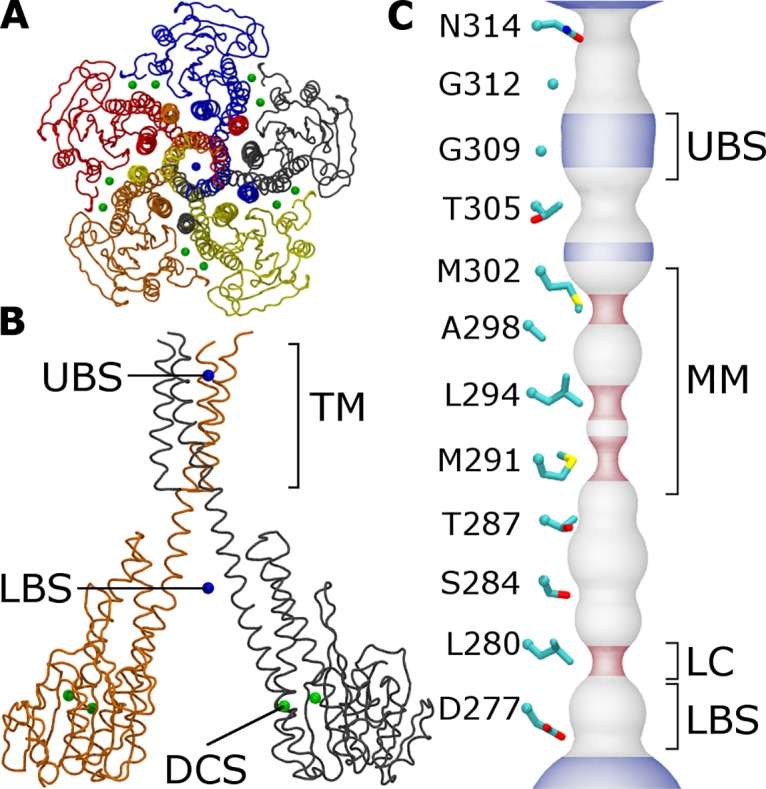
(A) Backbone trace of TmCorA viewed along the pore axis from the extracellular side, colored by protomer. Divalent cations in the 2HN2 crystal structure [13] are shown as spheres for (green) regulatory cations and (blue) cations inside the pore. (B) Side view of two protomers. Annotations include cation binding sites in the cytoplasmic domain and the upper and lower regions of the pore (respectively DCS, UBS, and LBS) and the transmembrane region (TM). (C) Surface representation of the pore diameter in the 2HN2 crystal structure [13]. The lower leucine constriction (LC) is indicated. The pore is colored by its local diameter, which is either (blue) larger than that of hexahydrated magnesium (0.68 nm), (red) smaller than that of a single water molecule (0.28 nm), or (grey) intermediate.
