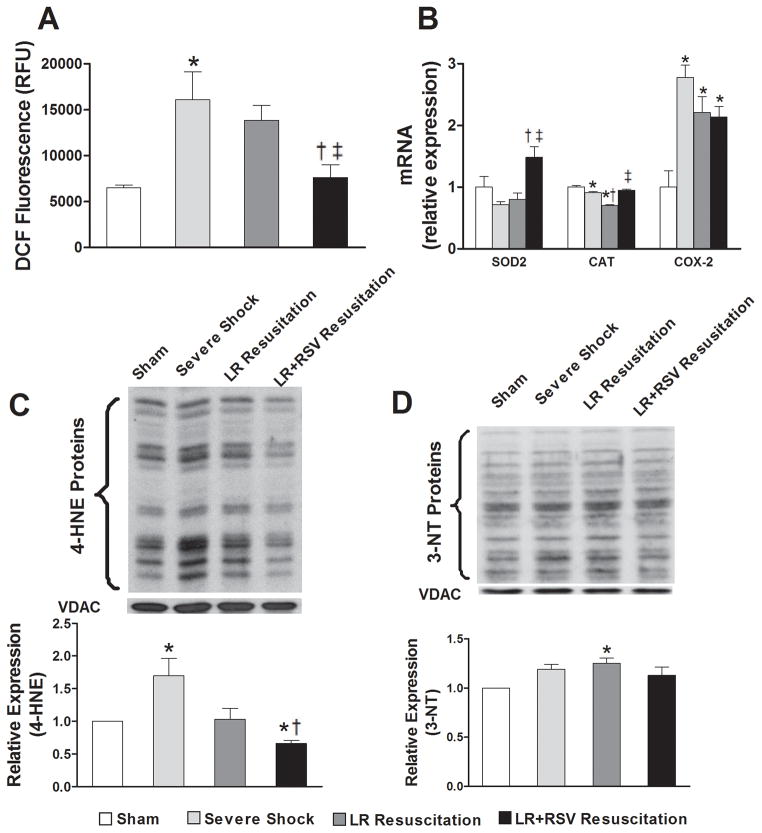
Figure 3. Resveratrol treatment during resuscitation ameliorated renal mitochondrial oxidative stress following hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation.
A, Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was detected by measuring the fluorescent signal from dichlorofluorescein. RSV supplementation significantly reduced the production of ROS following hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation. B, LR+RSV resuscitation significantly increased the mRNA expression of dismutase 2 (SOD2) and catalase (CAT) in kidney tissue when compared to LR resuscitation. C, 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) was measured by western blotas a marker of mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. 4-HNE levels robustly increased following Severe Shock and were significantly reduced with LR+RSV resuscitation. D, Expression levels of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) in mitochondria were determined by western blot. 3-NT levels increased with LR resuscitation, but did not increase with LR+RSV resuscitation. LR = Lactated Ringer’s solution; RSV = Resveratrol; COX = cyclooxygenase. Values are mean ± SEM. n = 6, *p<0.05 versus Sham; †p<0.05 versus Severe Shock; ‡p<0.05 versus LR Resuscitation.