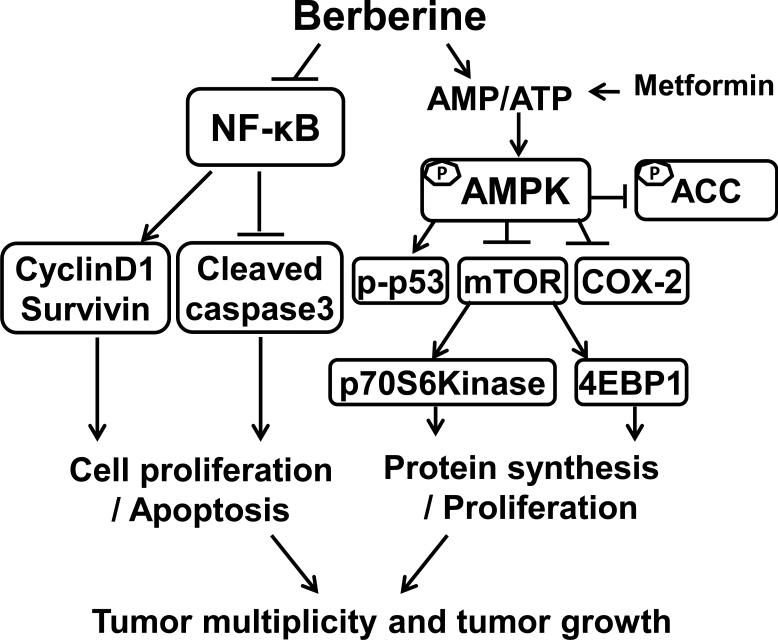
Figure 7. Mechanisms of berberine in suppressing colon cancer.
Berberine activated AMPK negatively regulates the mTOR signal pathway, resulting in inhibition of colon cancer proliferation and growth. Activated AMPK negatively regulates COX-2 in colon cancer. Activation of AMPK also induces phosphorylation of p53 which is a tumor suppressor. Inhibition of tumorigenesis by berberine is partially dependent on inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. This NF-κB suppression results in inhibiting transcription of NF-κB targets CyclinD1 and Survivin and stimulating the cleavage of caspase-3, modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. Interactions leading to activation of molecular targets are indicated by arrows; those that inhibited are indicated by a bar. Berberine modulation of both pathways leads to inhibition of tumor multiplicity and tumor growth.