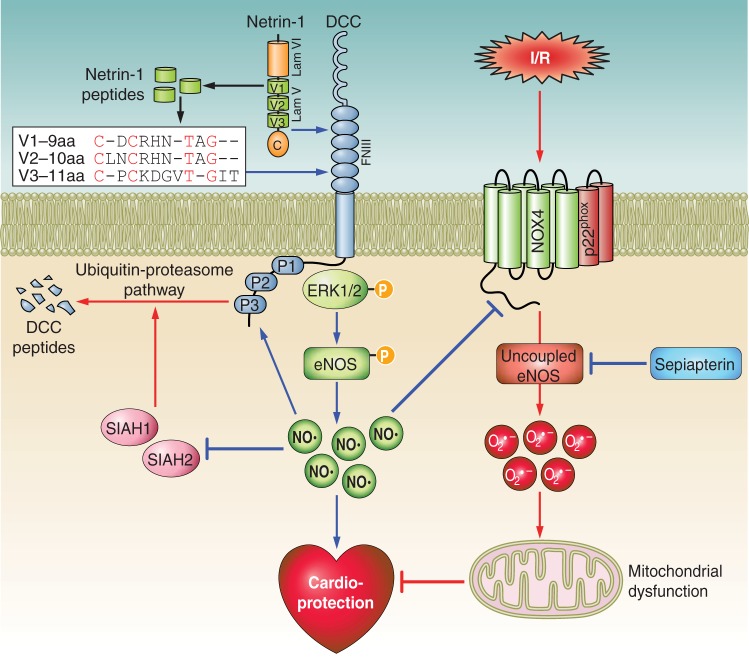
Fig. 1.
Molecular mechanisms of cardioprotection provoked by netrin-1 and netrin-1-derived small peptides. Netrin-1 or netrin-1-derived small peptides interact with their receptor DCC, leading to activation of ERK1/2 and eNOS, which increases production of NO, resulting in cardioprotection. NO downregulates SIAH, an E3 ligase for DCC, leading to reduced degradation of DCC by inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. This positive feedback mechanism augments cardioprotective signaling of netrin-1 and netrin-1-derived peptides by accumulation of the DCC receptor. At the same time, NO induced by netrin-1 or netrin-1-derived peptides also attenuates I/R injury by downregulation of NOX4, resulting in prevention of NOX4-dependent eNOS uncoupling and preservation of mitochondrial function, all of which contribute to cardioprotection. Cardioprotective pathways are highlighted in blue and myocardial ischemia-stress pathways in red.