FIGURE 4.
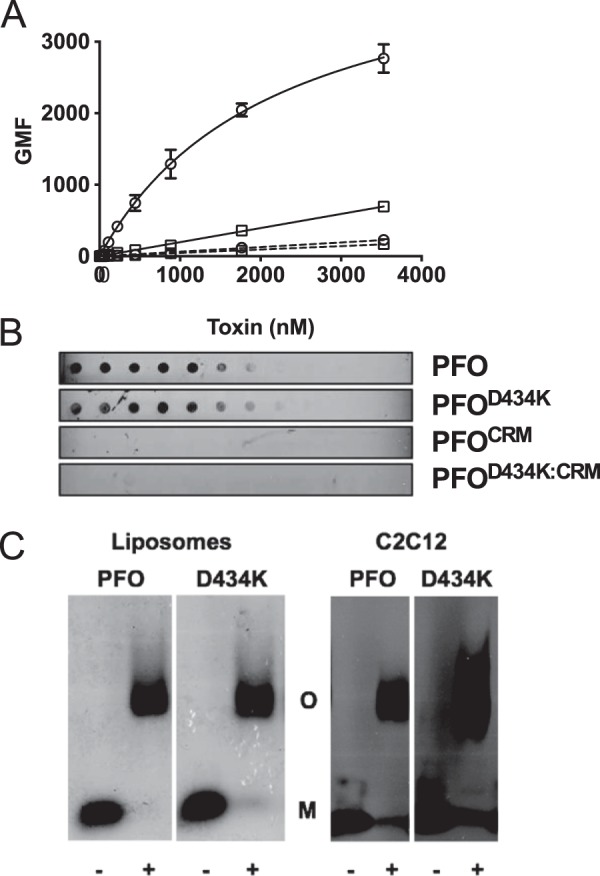
CDC membrane discrimination impacts cytolytic activity but not prepore formation. The CRM was substituted with glycines in wild-type PFO and PFOD434K backgrounds. Binding of each protein to murine C2C12 cells was determined by flow cytometry (A) and to pure cholesterol using a dot blot (B). PFO (squares), PFOD434K (circles), PFOCRM (squares with dashed line), PFOD434K:CRM (circles with dashed line). Results in A include standard error from at least two experiments. C, left panel: wild-type PFO or PFOD434K (17.6 μm) were incubated with or without cholesterol-rich liposomes and then the monomers and oligomers were separated by SDS-AGE. Gels were fixed, dried, and stained with Coomassie to visualize protein bands. Right panel: oligomer formation of PFO and PFOD434K (1.8 μmol) on C2C12 cells. Samples containing cell-bound toxin were separated by SDS-AGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. Toxin was detected using anti-PFO serum. The + or − denoted at the bottom of the panels indicates whether the toxin was incubated with or without liposomes (left panel) or C2C12 cells (right panel). Densitometric analysis shows (56) that 85–90% of the PFO and PFOD434K monomers were converted to SDS-stable oligomers. M, monomer. O, oligomer.
