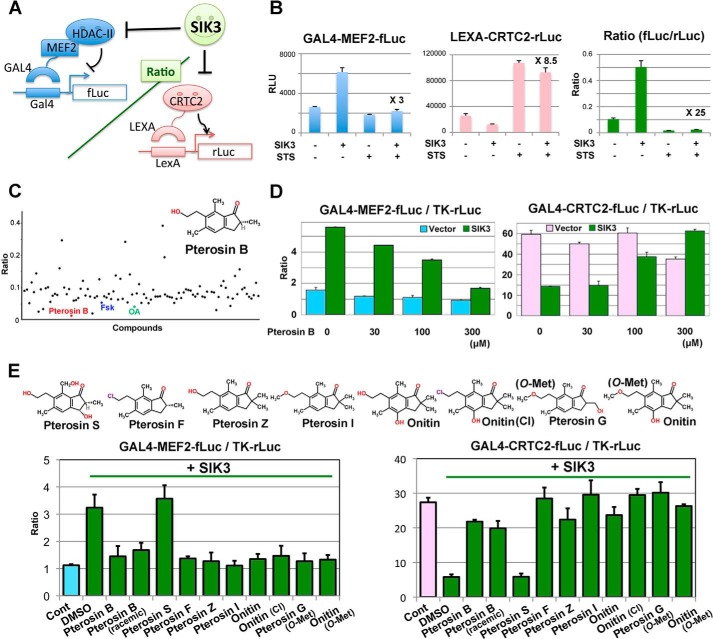
FIGURE 3.
Pterosin B inhibits SIK3 signaling. A, a principle of reporter-based chemical screening. B, a model experiment of reporter assays using the nonspecific kinase inhibitor STS (10 nm). The fold difference in un-normalized luciferase activities between SIK3 overexpression alone and SIK3 + STS is indicated (n = 3). C, the result of a representative plate containing pterosin B is indicated. Fsk (20 μm) and okadaic acid (OA, 1 μm) are positive controls for SIK3 inhibition. Compounds were classified into kinase inhibitors, uncharacterized compounds, and natural compounds and were treated for 36 h at 10 μm, 10 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ml, respectively. Some compounds showed high ratios caused by errors, such as cell toxicity. D, MEF2 and CRTC2 activity were measured in the same GAL4-based firefly luciferase system in the AML-12 cells. E, structural activity relationship of pterosin B and its derivatives. HEK293 cells were transformed with the MEF2 or CRTC2 reporter together with the SIK3 expression vector. Compounds (300 μm) were treated for 36 h. n = 2–3. Cont, control.