FIGURE 1.
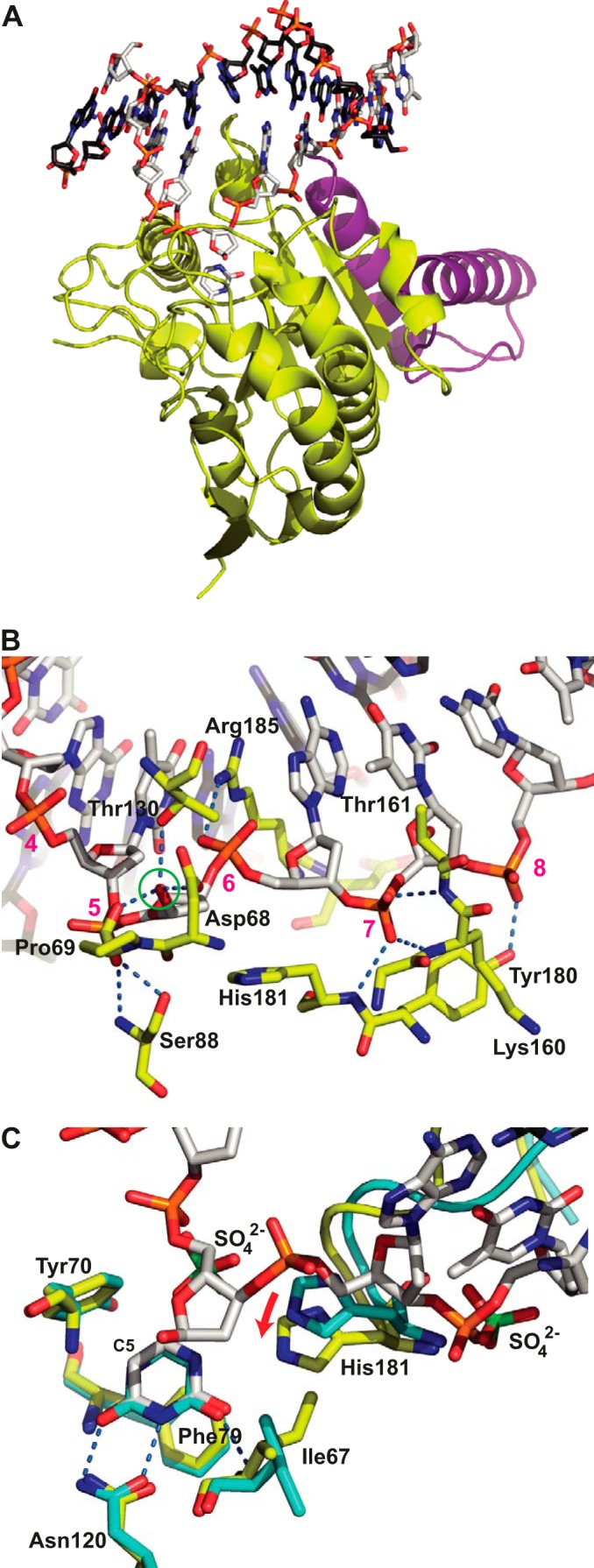
Structure of the His-D4·A201–50·DNA complex. A, D4 is shown with yellow carbon atoms, A201–50 is in violet, the uracil molecule is in stick representation with white carbon atoms, and the dsDNA oligomer is in stick representation with white carbon atoms for the cognate strand and black carbon atoms for the complementary strand. B, detail of the D4·DNA interaction. The residues from D4 involved in hydrogen bonds with the phosphate backbone or the OH1′ hydroxyl group of the extrahelical α-deoxyribose (green circle) are shown in stick representation using the coloring scheme described above for A. Their hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted blue lines. Nucleotides of the cognate strand are numbered in magenta. C, comparison of the uracil binding site of the 1.85 Å structure of His-D4·A201–50 soaked with uracil (cyan carbon atoms) to the same site of the His-D4·A201–50·DNA complex colored as before. The hydrogen bonds involving the uracil molecule are indicated. Sulfate ions (green sulfur atoms) arising from the crystallization solution in the His-D4·A201–50 structure are shown together with the DNA in the DNA-complex structure. Note the 1.6 Å movement of His-181 upon DNA binding (red arrow). The active site residues Asp-68 and Pro-69 are hidden for clarity. The complex formed by chains A, B, C, and D of the crystal structure (Protein Data Bank entry 4YIG) has been used throughout the analysis.
