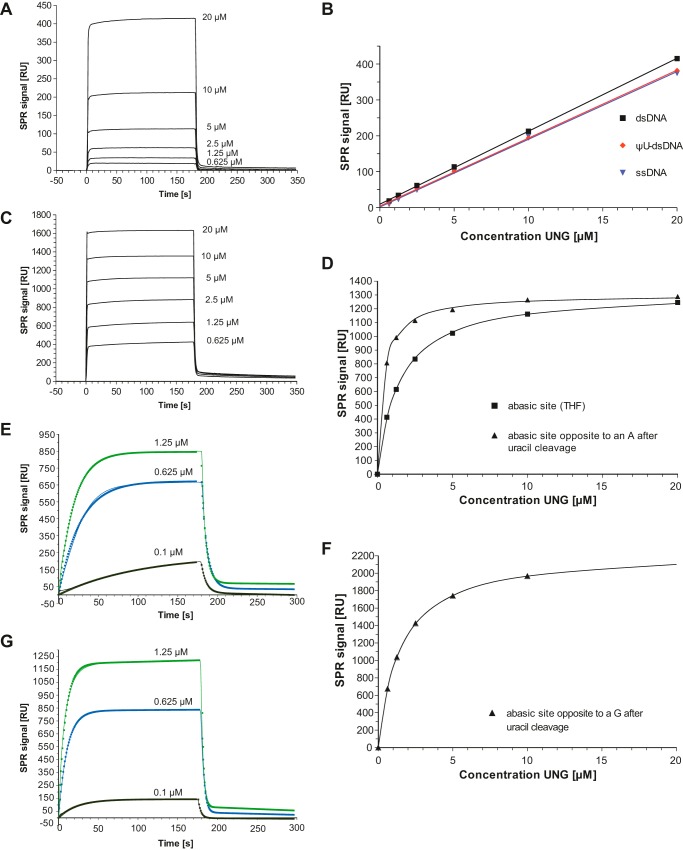
FIGURE 5.
Study of His-D4·A201–50 binding to DNA by SPR. Kinetic parameters are given in Table 2. A, sensorgrams of increasing His-D4·A201–50 concentrations binding to immobilized unmodified 30-mer dsDNA. B, binding of His-D4·A201–50 to immobilized 30-mer: unmodified dsDNA, ΨU-containing dsDNA and ssDNA. A linear fit to the concentration-dependent binding is shown. C, sensorgrams of increasing His-D4·A201–50 concentrations binding to immobilized 30-mers dsDNA containing a THF abasic site. D, fit of an equilibrium binding model to the plateau values of His-D4·A201–50 binding to THF abasic sites (see C) and to abasic sites produced from uracil containing dsDNA. E, binding of His-D4·A201–50 to a uracil containing 30-mer dsDNA (continuous thin lines). Experiments use different flow cells of a CM5 chip. Sensorgrams have been fitted with a single exponential for the association phase and an exponential decay combined with a linear function for the decay phase. The points of the fitted functions are shown. F, fit of an equilibrium binding model to the plateau values obtained for His-D4·A201–50 binding to abasic sites produced from dsDNA with a U:G mismatch. G, binding of His-D4·A201–50 to a uracil containing 30-mer dsDNA with a U:G mismatch analyzed as in E.