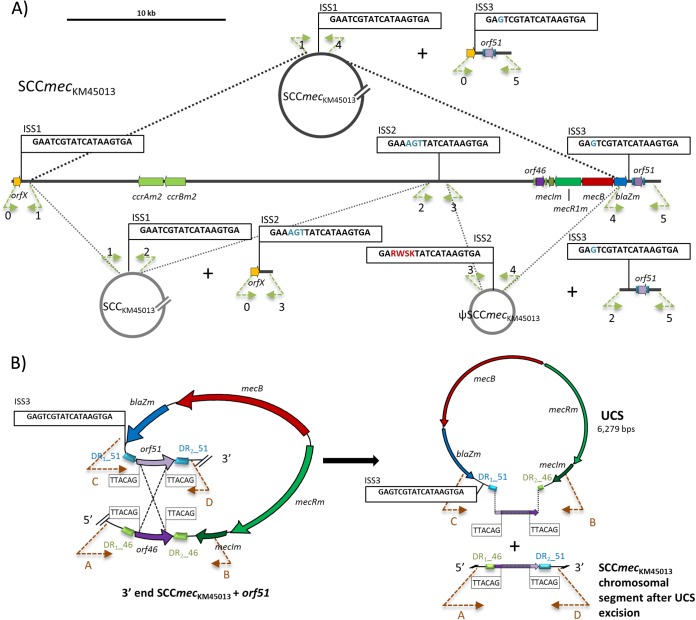
FIG 3.
Graphical representation of the spontaneous circular chromosomal excisions detected in SCCmecKM45013. (A) Display of the circular intermediates (CIs) designated to those with integration site sequences (ISSs) as delimiting region (SCCmecKM45013, SCCKM45013, and ΨSCCmecKM45013), and the resulting chromosomal regions after spontaneous loss. The arrows indicate the extent and direction of transcription of orfX, orf46, and orf51, the site-specific recombinase genes (ccrAm2, ccrBm2), and the genes comprising the mecB operon (mecIm, mecRm, mecB and blaZm). ISS1 to ISS3 are boxed. Bases in blue indicate divergences from ISS1, while letters in red indicate the presence of double peaks (Sanger sequencing) in the sequence chromatograms: R (G or A), W (A or T), S (G or C), and K (T or G). A size scale in kb is displayed in the upper left-hand corner. (B) Spontaneous chromosomal excision of an unconventional circularizable structure (UCS) carrying the mecB complex. The left panel shows the potential homologous recombination event between orf46 and orf51 in M. caseolyticus strain KM45013. The right panel shows the resulting UCS and the chromosomal region after excision. The recombined area is colored in purple with white dots. The imperfect direct repeats (DR1, DR2) flanking orf46 and orf51 are indicated as blue (DR_51) or green (DR_46) blocks. The suggested recombination sites (5′-TTACAG-3′) and the ISS3 are indicated within black boxes. Primers used to detect the different circularized elements and the excision sites are indicated as dashed arrows, with the arrowhead indicating the direction of amplification. They are named 0 to 5 for the named CIs and A to D for the designated UCS. See Table S1 in the supplemental material for nomenclature.