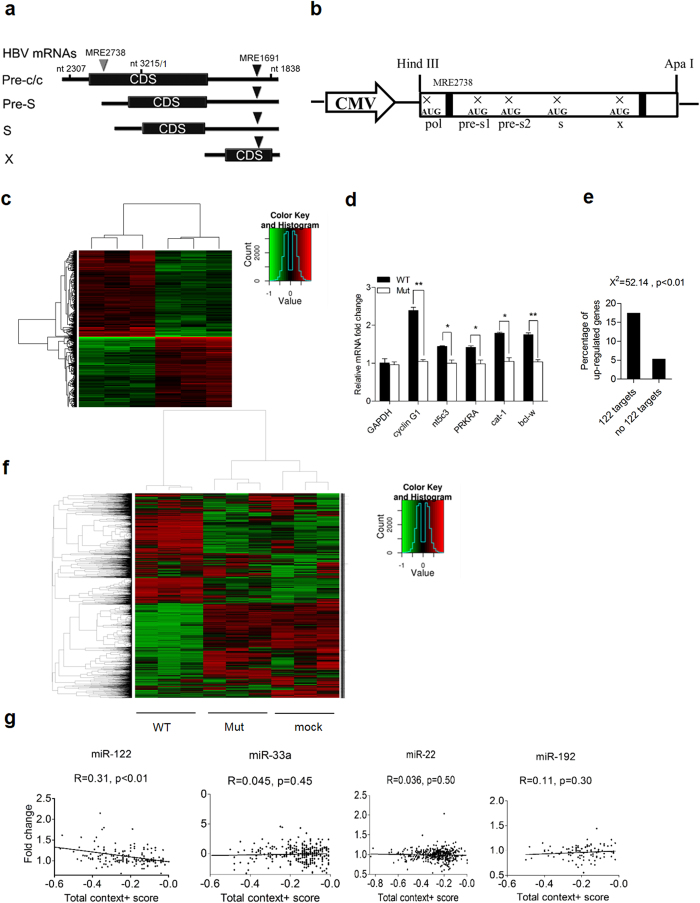
Figure 3. HBV mRNAs affect expression of host genes.
(a) Schematic representation of the fragment of HBV pgRNA (spanning nucleotides 2307-3215 and 1-1838) used in this study. The fragment contains miR-122 response elements and most sequences of major viral mRNAs. ▼ represents the miR-122 response elements. (b) Diagram of HBV pgRNA fragment expression constructs. The fragment of HBV pgRNA (spanning nucleotides 2307-3215 and 1-1838) was inserted into the pcDNA3.1 plasmid, downstream of the CMV promoter, Hind III and Apa I sites. The start codon of Pol, PreS1, PreS2, S and X were mutated, producing the WT construct. (c) Shown is hierarchical clustering analysis of transcripts differentially expressed in Huh7 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 carrying the HBV pgRNA fragment (WT) or the empty pcDNA3.1 vector as a mock. The values from three independent experiments are displayed. (d) Quantification of miR-122 targets by real-time PCR in Huh7 cells treated as in c. Data shown are the means ± SD for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (e) Distribution of up-regulated transcripts (fold change >1.25) between miR-122 predicted targets and no miR-122 predicted targets. (f) Hierarchical clustering analysis of differentially expressed transcripts. Huh7 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 carrying the wild type (WT) or mutant (Mut) HBV pgRNA fragment within miR-122 response elements or the empty pcDNA3.1 vector as a mock. The values from three independent experiments are displayed. (g) The fold change of predicted targets of miR-122, miR-33, miR-22, and miR-192 were plotted based on their context+ scores. Values of the correlation coefficient (R) and P are shown.