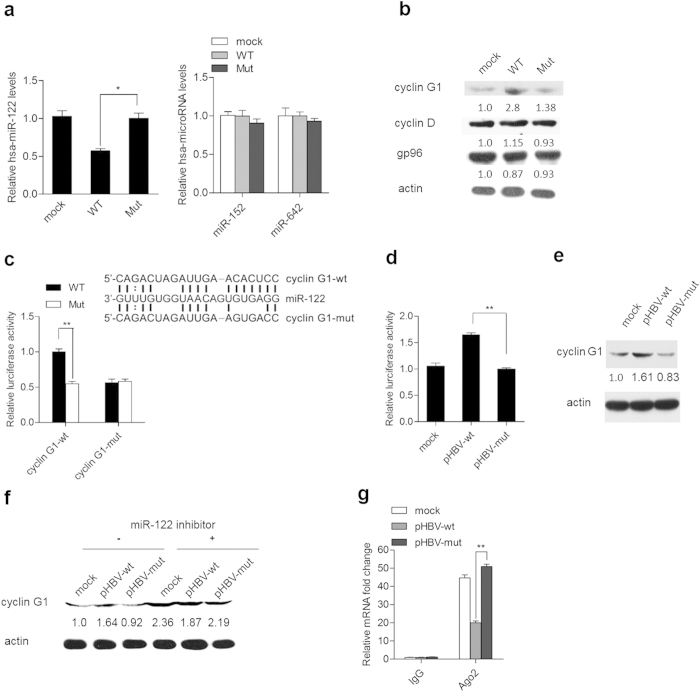
Figure 4. HBV mRNAs up-regulate cyclin G1 in a miR-122 response element-dependent manner.
(a) Huh-7 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 carrying the wild type (WT) or mutant (Mut) HBV pgRNA fragment or with the empty plasmid as a mock, and miR-122 levels were quantified by real-time PCR. The levels of miR-152 and miR-642 were quantified as negative controls. (b) Western blot analysis of cyclin G1 in Huh7 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 carrying the wild type (WT) or mutant (Mut) HBV pgRNA fragment or the empty pcDNA3.1 vector as a mock. The cyclin D and gp96 protein levels were also assessed as negative controls. (c) Schematic representation of the miR-122 binding site (cyclin G1-wt) within the 3’UTR of cyclin G1 mRNA; the introduced mutations (cyclin G1-mut) are indicated (the frame). Huh7 cells were co-transfected with pcDNA3.1 carrying the wild type HBV pgRNA fragment and a firefly luciferase reporter plasmid with a 3’UTR containing either a cyclin G1-wt or cyclin G1-mut sequence. At 48 h post-transfection, the firefly luciferase and renilla luciferase activities were measured using a dual-luciferase assay kit. (d) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with the cyclin G1 wild type 3’UTR reporter and wild type (pHBV-wt) or mutant (pHBV-mut) HBV replication plasmid or pcDNA3.1 as a mock. At 48 h post-transfection, firefly luciferase and Renilla luciferase activities were measured, and the firefly luciferase activity was normalized to that of Renilla luciferase. (e) Huh7 cells were transfected with pHBV-wt, pHBV-mut, or pcDNA3.1 as a mock. At 48 h after transfection, cyclin G1 protein levels were measured by immunoblotting. Actin was used as a loading control. (f) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with pHBV-wt, pHBV1.3-mut, or pcDNA3.1 as a mock, along with miR-122 inhibitor or a randomized oligonucleotide (control). Western blot analyses were subsequently performed for cyclin G1. (g) Lysates from Huh7 cells transfected with pHBV-wt, pHBV-mut, or pcDNA3.1 as mock underwent immunoprecipitation with anti-Ago2 antibody or control IgG. Immunoprecipitated RNAs were recovered, and quantitative real-time PCR was performed for analysis of miR-122 binding sites in the cyclin G1 3’UTR. Data shown are the means ± SD for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.