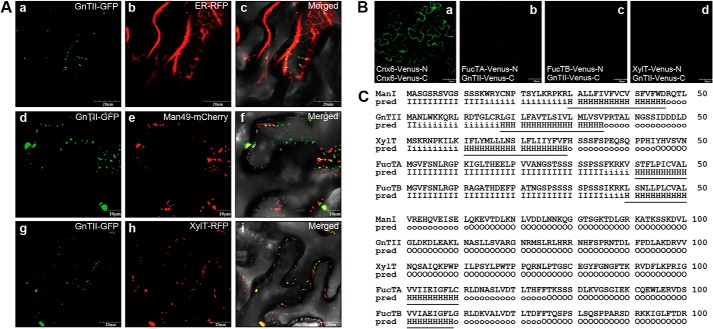
FIGURE 6.
GnTII is positioned in the cis-half of the Golgi in a kin-independent manner. A, subcellular localizations of GnTII-GFP, XylT-GFP, FucTA-GFP, and FucTB-GFP are compared with those of ER-RFP (ER marker), Man49-mCherry (cis-Golgi marker), and XylT-RFP (medial-Golgi marker), respectively. Left column, GFP fluorescence obtained with GnTII-GFP (panels a, d, and g); middle column, signals from ER-RFP, Man49-mCherry, and XylT-RFP (panels b, e, and h); right column, overlay of both signals (panels c, f, and i). The indicated fusion constructs were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana epidermal cells and analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Scale bars, 50 μm. B, BiFC assay. The indicated fusion constructs of Venus-N and Venus-C were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana epidermal cells. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was used for visualization of fluorescence reporting protein-protein interactions. The fluorescence of Cnx6-Venus-N and Cnx6-Venus-C was used as a positive control for the BiFC experiment (panel a). Combinations of the indicated constructs did not produce Venus fluorescence (panels b–d). Scale bars, 10 or 20 μm. C, predicted length of transmembrane helices and topology. The transmembrane helices and topology of GnTII, XylT, FucTA, and FucTB were analyzed at the HMMTOP server. The N-terminal regions predicted (pred) as transmembrane helices are indicated with underlining. I, cytosolic domain; H, transmembrane helix; O, extracellular domain.