FIGURE 4.
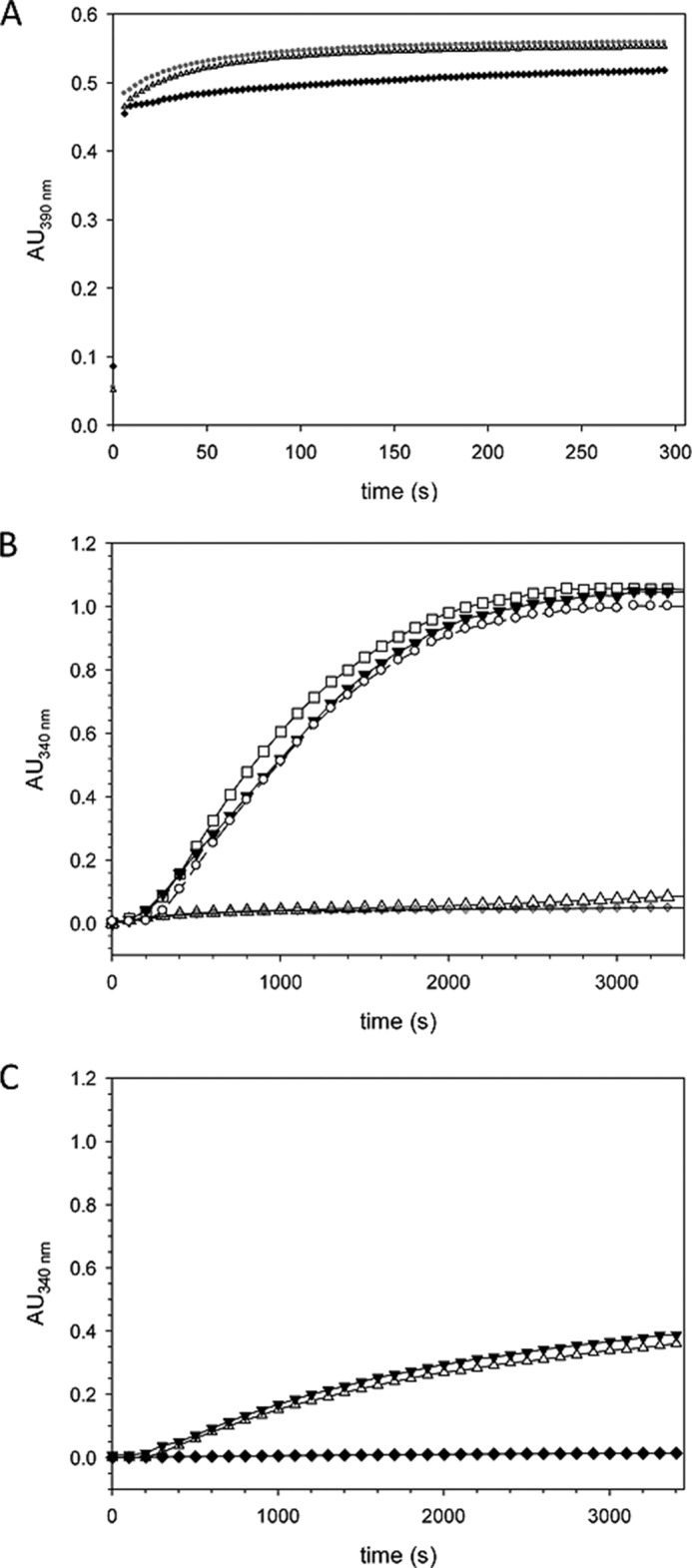
Ca2+/CaM inhibits Par17-catalyzed tubulin assembly in an in vitro tubulin polymerization assay. A, the PPIase activity of Par17 in the presence of Ca2+/CaM was determined using a protease-coupled assay that employs as substrate the oligopeptide succinyl-AKPF-4-nitroanilide, as previously described (20). The PPIase activity of Par17 was measured in a reaction mixture containing 2 μm GST-Par17 and 1 mm CaCl2 either with (▴) or without (●) 15 μm CaM. The uncatalyzed cis-to-trans isomerization in the absence of Par17 is shown as a control (♦). Calculation of the first-order rate constants for the cis/trans isomerization (1.47 ± 0.02 × 10−2 in the presence and 1.5 ± 0.03 × 10−2 in the absence of Ca2+/CaM) indicated that Ca2+/CaM does not affect Par17 PPIase activity (insensitivity of Par17 and CaM to proteolytic digestion by α-chymotrypsin was verified for the duration of the measurements). B, assembly of microtubules was initiated by dilution of ice-cold tubulin to a final concentration of 6.7 μm in 80 μl of G-PEM buffer set to 37 °C. Polymerization was measured in absence of Par17 (♦) and in presence of 16 μm GST-Par17 (▾), 16 μm GST-Par17, and 1 mm Ca2+ (○) and 16 μm GST-Par17 and 30 μm CaM (□) as well as 16 μm GST-Par17, 1 mm Ca2+, and 30 μm CaM (▵). C, tubulin polymerization was monitored in absence of GST-Par14 (♦), in the presence of 16 μm GST-Par14 (▾), and in presence of 16 μm GST-Par14, 1 mm Ca2+, and 30 μm CaM (▵). AU, absorbance units.
